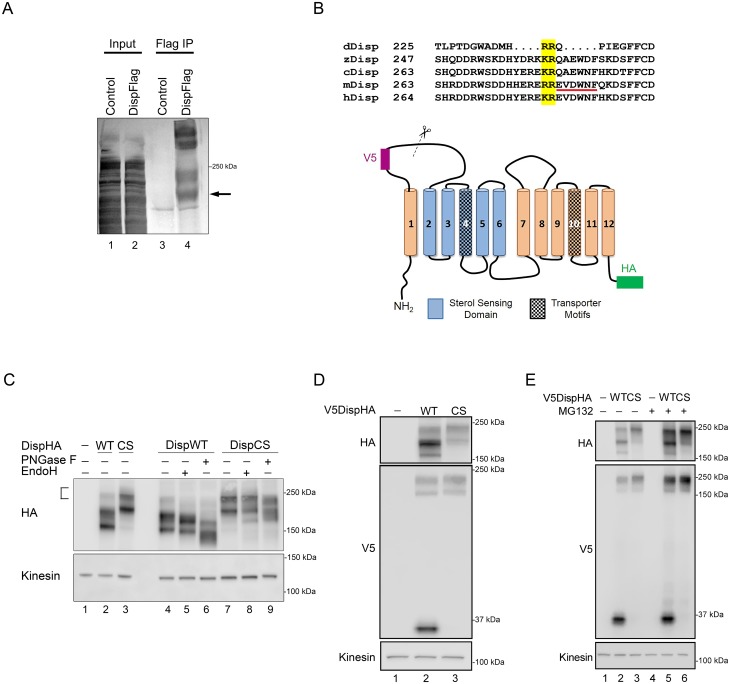
Figure 2. Disp is cleaved at a Furin consensus sequence in EC1.
(A) Disp-Flag was expressed in HEK293T cells, immunopurified from cell lysates on Flag beads and the 145 kDa species (arrow) excised and analyzed by Edman degradation. (B) Alignment of EC1 sequence from Disp proteins of Drosophila, zebrafish, chick, mouse and human. Edman sequencing of murine Disp145 revealed EVDWNF (red line) to be the amino terminal sequence, suggesting that cleavage occurs adjacent to dibasic residues R279 and E280 (yellow box). A diagram of murine Disp shows V5 and HA epitope tag insertion sites, functional domains and the approximate location of the identified cleavage motif in predicted EC1 (scissors). (C) Cell lysates from NIH3T3 cells expressing wild type or cleavage site mutant (CS, R279A/E280A) were treated with deglycosylating enzymes. The bracket indicates the ~250 kDa fraction. (D) Lysates from NIH3T3 cells expressing wild type or cleavage site mutant V5DispHA proteins were examined for presence of the 30 kDa V5 fragment by western blot. (E) NIH3T3 cells expressing wild type or CS mutant Disp proteins were treated for ~6 hr with DMSO vehicle or MG132 proteasome inhibitor. Kinesin is the loading control.