Figure 5. Creation of an OGG1-plasmid DNA crosslink substrate.
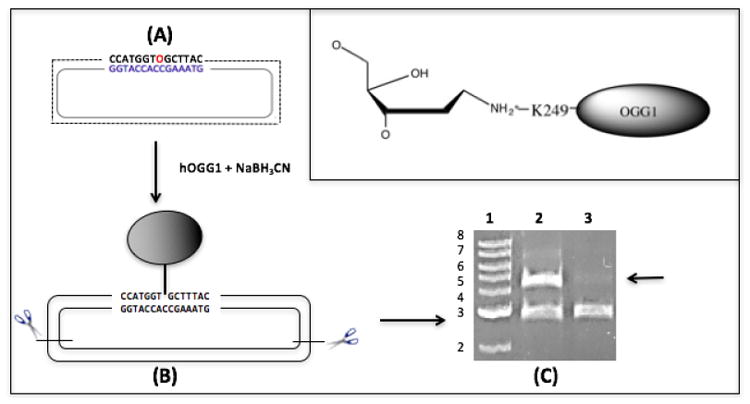
(A) Plasmid DNA containing an 8-oxo-dG residue (O, in red) was reacted with OGG1 in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride to create a covalent bond between lysine residue 249 and a deoxyribosyl moiety on the plasmid (see Methods for details, chemical structure depicted in inset). (B) This product was cut with restriction enzymes to generate two fragments: a 2800 bp protein-free DNA fragment and a 4400bp fragment crosslinked to OGG1. (C) The restriction digested material was resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis prior to (lane 2) or following (lane 3) precipitation in the presence of K-SDS (see Methods), and stained with ethidium bromide. The arrow illustrates the selective loss of the OGG1-crosslinked DNA fragment following K-SDS precipitation. Lane 1; molecular weight marker in kilobase pairs.
