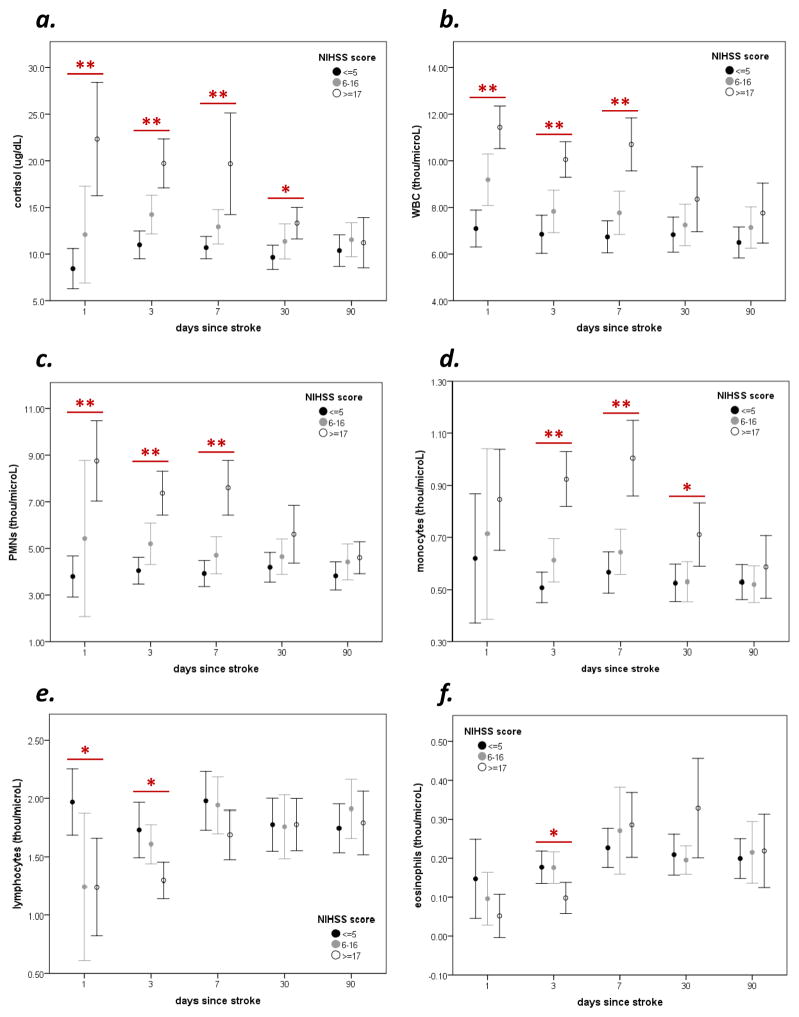
Figure 1.
Patients with severe stroke (NIHSS≥17) experience a prolonged increase in cortisol (a) as well as an increase in the overall numbers of white blood cells (b), neutrophils (d) and monocytes (d). Severe strokes are also associated with a less prolonged decrease in the numbers of lymphocytes (e) and eosinophils (f). Statistics are by ANOVA; *P<0.05, *P<0.01.