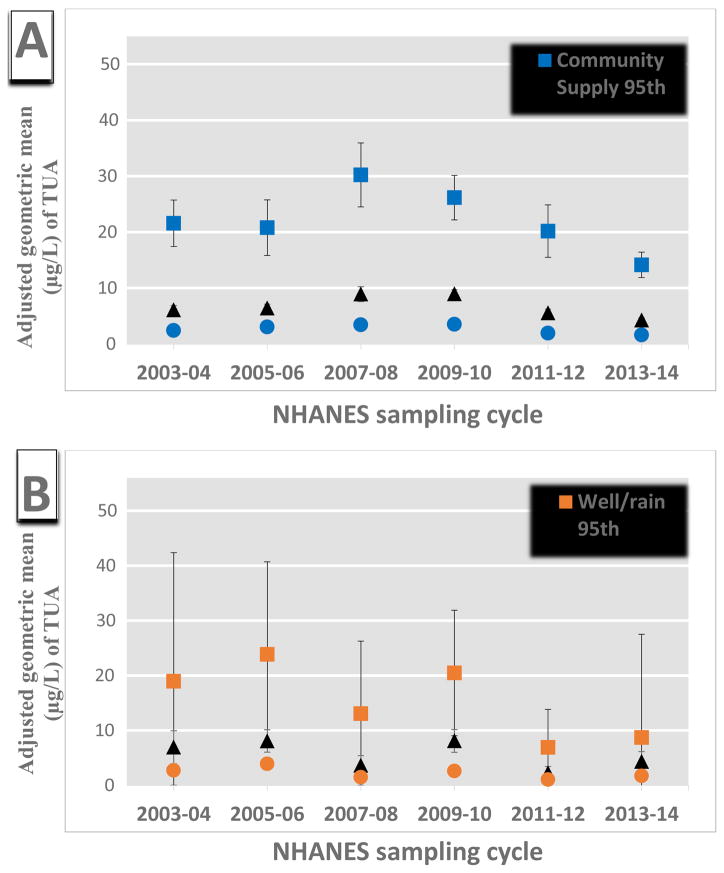
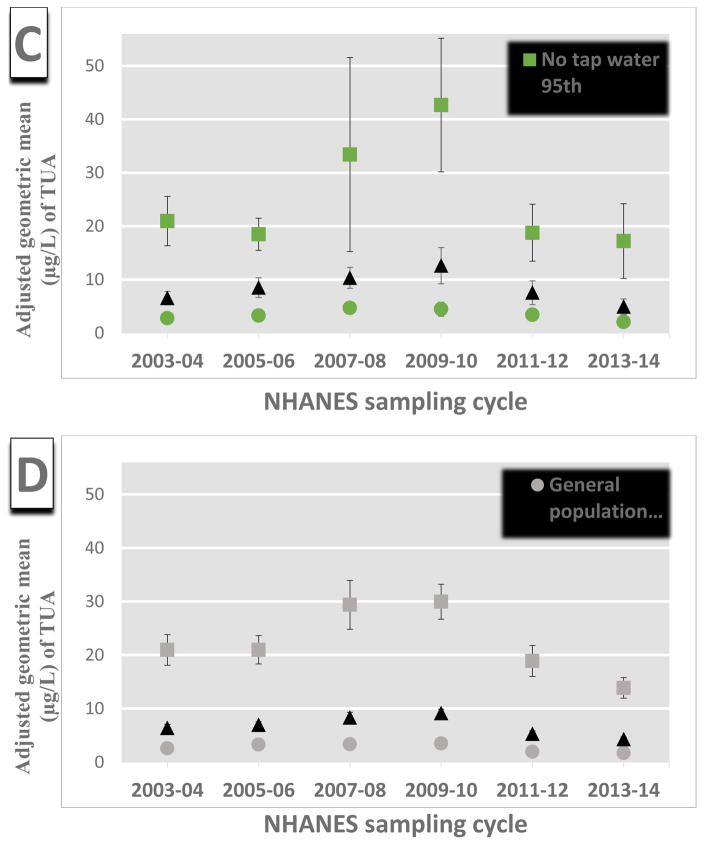
Figure 1.
Association between adjusted weighted geometric means of urinary arsenic (μg/L) and NHANES cycles in the general U.S. population by percentiles of exposure (i.e. 95, 75, 50th) for those who consume tap water from a (A) community supply (n=3,427), (B) well or rain cistern (n=506), or (C) do not consume tap water (n=1,060), and (D) among the general U.S. population (n=4,993). The population is restricted to those individuals with urinary AsB concentrations below the limit of detection (i.e. ≥0.84) Estimates are from linear multivariate regression model with an interaction term between NHANES sampling cycle and tap water source adjusted for log-transformed urinary creatinine (continuous), age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI (categorical), PIR, type of water consumed (categorical), recent smoking, and consumption of seafood, rice, poultry, or juice.. Urinary arsenic is defined as total urinary arsenic (TUA) which is total arsenic minus AsB and AsC.