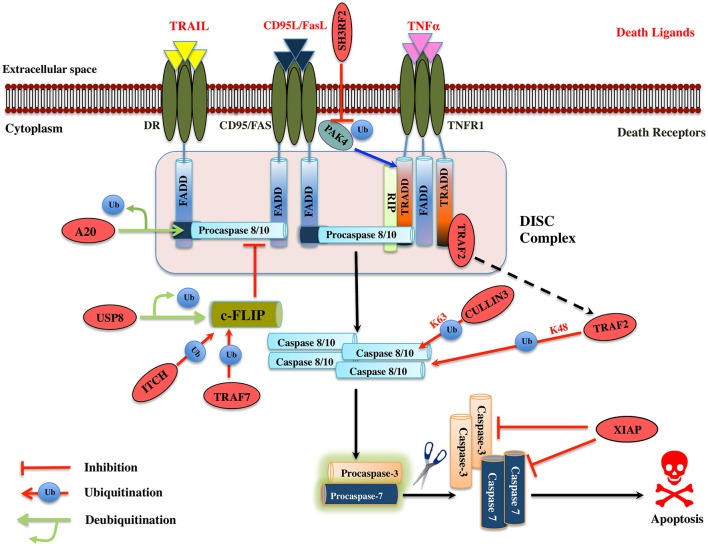
Figure 4.
Illustration of E3 ligases and DUBs that regulate extrinsic pathway of Apoptosis. Signaling molecule such as Fas ligand, TNF (Tumor necrosis factor) and TRAIL (TNF related apoptosis-inducing ligand) bind to the transmembrane death receptors like FasR, TNFR, death receptor 4/5, respectively to induce the extrinsic apoptosis pathways. TNF extrinsic apoptosis pathway is initiated by binding of TNF ligand to it two cognate surface receptors, TNF-R1 and TNF-R2. Ligand binding to TNF-R1 results in the dissociation of the SODD (silencer of death domains) from the cytoplasmic tail of TNF-R1 and this facilitates recruitment of adaptor protein TRADD (TNFR1-associated death domain protein). This association further leads to the recruitment of FADD (Fas-associated death domain protein), TRAF2 (TNFR-associated factor 2), TRAF5, RIP (receptor-interacting protein), and c-IAP1/2 (cyto inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) and forms a DISC (death-inducing signaling complex). DISC mediates the enrolment of additional proteins such as the initiator caspase, procaspase-8, which, then proteolytically cleaved, releases an active form of caspase-8, which further activates the effector caspase-3 and 7 and leads to the apoptosis. Activation of caspase-8 is regulated by c-FLIP (cellular Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin 1β-converting enzyme inhibitory protein), a catalytically inactive homolog of caspase 8 that interacts with procaspase-8. Several IAPs (inhibitors of apoptosis) also regulate apoptosis by interacting with TRAF2. Similarly, when Fas protein binds to FasL, it promotes the recruitment of FADD adaptor protein that has DD (Death domain) and DED (Death effector domain) that associate with caspase-8 and 10 and forms a DISC (Hongmei, 2012). Later, apoptosis is preceded just same as in TNF signaling. Several ubiquitin ligases and DUBs that are involved in the pathway and critically regulating the apoptosis are shown as red ovals.