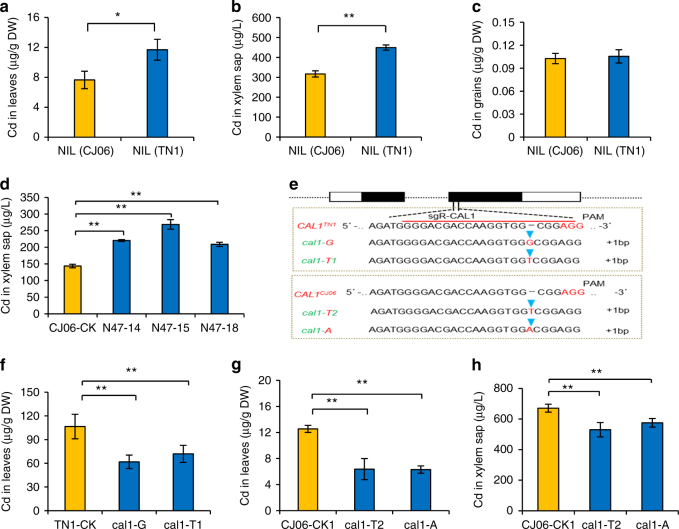
Fig. 2.
CAL1 positively regulates Cd contents in rice leaf and xylem sap. Leaves and xylem sap were collected from 2 weeks old seedlings exposed to 10 µM Cd for 7days, and grains was sampled from rice plants grown in Cd-contaminated paddy soil. a–c Cd levels in leaves (a), xylem sap (b) and grains (c) from NIL(TN1) and NIL(CJ06). d, e determination of Cd contents in xylem sap (d) of the CAL1-complementation lines N47-14, N47-15, and N47-18, which simulate overexpression lines due to increased expression of CAL1 (Supplementary Fig. 3d) in CJ06 background. CJ06-CK represent transgene-negative controls. e Identification of cal1 mutants generated by CRISPR/Cas9. cal1-G and cal1-T1 represent mutants with single G or T insertion in CAL1 coding region, respectively, with TN1 background. cal1-T2 and cal1-A represent mutants with single T or A insertion in CAL1 coding region, respectively, with CJ06 background. f–h Cd contents in leaves (f, g) and xylem sap (h) of cal1 mutants. TN1-CK and CJ06-CK1 represent transgene-negative controls. Data are mean ± SD, n = 3 in (a–c), or 4 in (d and f–h). Significant differences were determined by Student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)