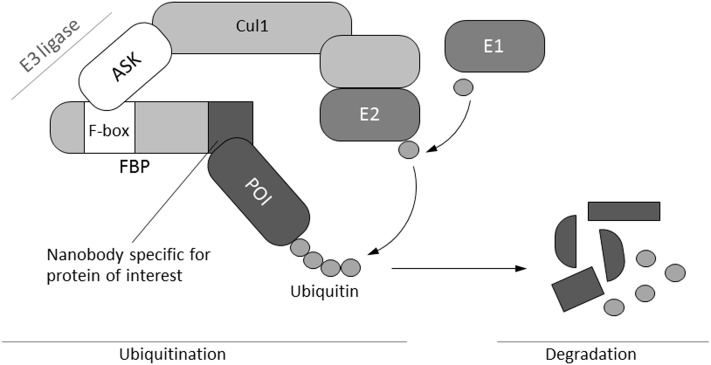
FIGURE 1.
Schematic illustration of the mechanism of selective protein degradation. Protein degradation by the ubiquitin pathway is carried out by a complex cascade of enzymes (E1–E3) that catalyze the covalent attachment of multiple ubiquitin molecules to the target protein. Subsequently, polyubiquitinated proteins are degraded by the proteasome. The N-terminal F-box domain typically binds to one of the members of the ASK family, whereas the C-terminal part determines substrate specificity via different protein–protein interaction motifs. These motifs are replaced by a nanobody specific for a protein of interest in order to engineer a molecular tool for selective protein depletion (Caussinus et al., 2011). Cul1, cullin; FBP, F-box protein; ASK, Arabidopsis-S-phase kinase-associated protein (SKP1)-like; E1, ubiquitin activating enzyme; E2, ubiquitin conjugating enzyme; E3-ligase, ubiquitin ligase; POI, protein of interest.