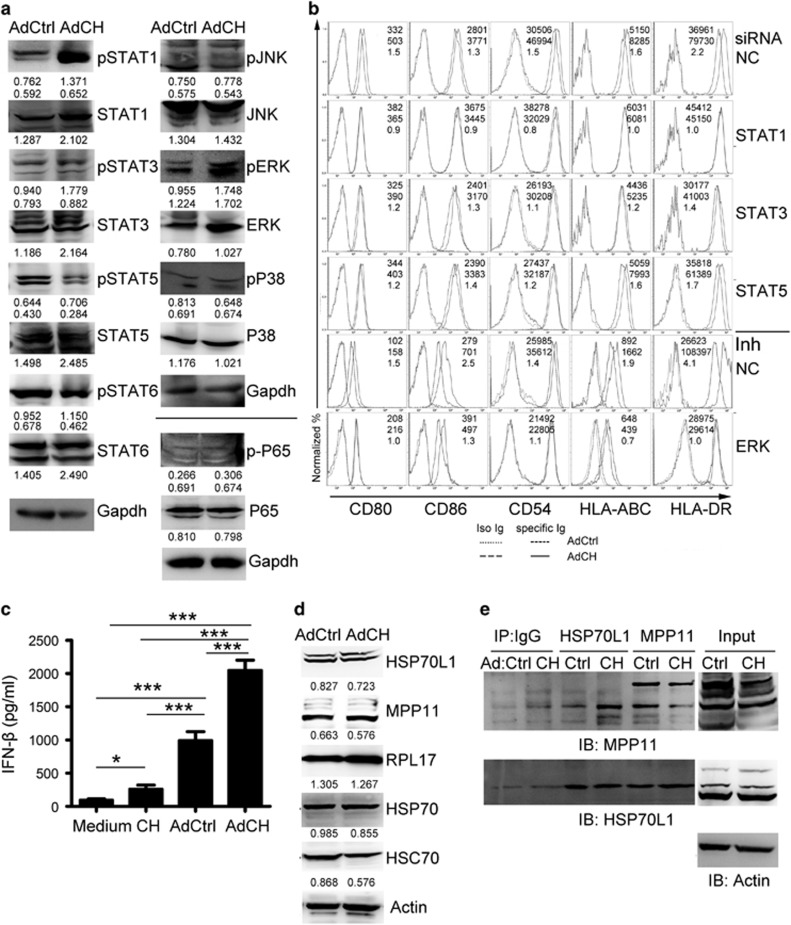
Figure 5.
The pathways of STAT1 and ERK involved in the maturation of AdCEA576–669HSP70L1-DCs. (a, d, e). Immature DCs were transfected with indicated Ad for 24 h, and then the expression or/and phosphorylation of STAT1,3,5,6, ERK, JNK, P38 and P65 (a) and of HSP70L1, MPP11, HSP70, HSC70 and RPL17 (d) was detected using western blot, and the interaction between HSP70L1 and MPP11 was detected using CoIP/western blot (e). (b) Immature DCs were transfected with indicated siRNA (20 nM) or ERK inhibitor (UO126,10μM) 2 h before with indicated Ad for another 48 h, and then the phenotype of DCs was detected using FACS. (c) Immature DCs were pulsed with CEA576–669HSP70L1 (CH) or transfected with indicated Ad for 18 h, and then the production of IFN-β was detected using ELISA. Representative results of three (a–d) or two (e) independent experiments are shown. Values are relative gray-intensity to GAPDH (a, up), corresponding total protein (a, below) or to Actin (d) using the ImageJ software, mean fluorescence intensity (AdCtrl, up; AdCH, middle) and mean fluorescence intensity ratio (bottom) of AdCH/AdCtrl (b), or mean±s.e.m. (c). CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; IFN, interferon; MPP11, M-phase phosphoprotein 11; siRNA; short interfering RNA.