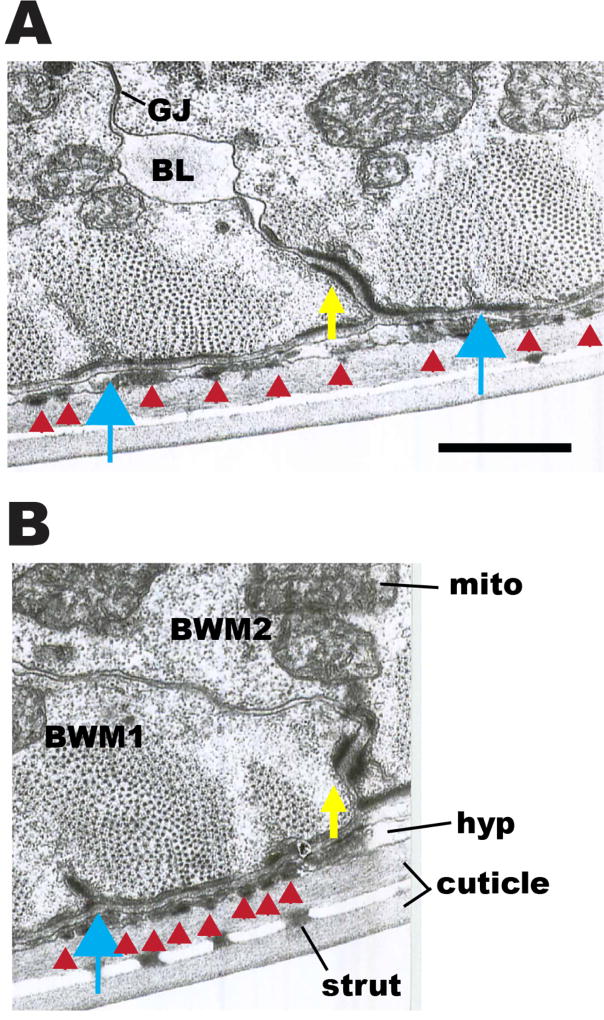
Figure 11. Transmission EM images of boundaries between adjacent body wall muscle cells.
(A) and (B): Two cross-sectional views of body wall muscle, showing portions of two adjacent muscle cells. Yellow arrows point to electron dense material at basolateral membranes between two adjoining muscle cells (BWM1, BWM2). Discontinuous patches of this dense material can be followed along cell borders in serial thin sections to lead up to dense bodies (blue arrows), and for the most part the same proteins localize to this zone as for dense bodies. Flat black bars of electron dense material (red arrowheads) are also seen on the basal membrane of the muscles beneath each sarcomere, and filling the thin hypodermal layer (hyp) coincident with the sarcomeres; these represent attachment points between muscle, hypodermis and cuticle. Some basal lamina material (BL) projects inward from the basal zone between muscle cells and can collect in spaces along their lateral borders. Cuticle has an inner and outer layer, connected by struts. Mito, mitochondria. GJ, gap junction. Scale bar, 1 µm.