Figure 6.
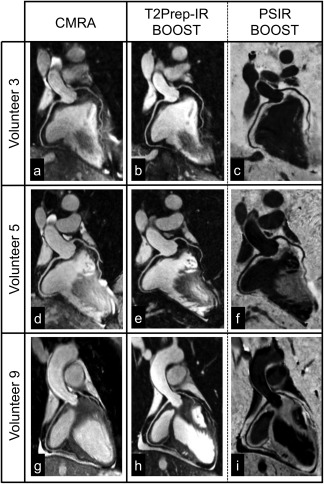
Reformatted coronary depiction in three representative healthy volunteers obtained with a conventional T2‐prepared bright‐blood CMRA acquisition (a, d, g) and the proposed BOOST sequence for simultaneous bright‐blood (T2Prep‐IR BOOST datasets in b, e, h) and black‐blood (PSIR BOOST datasets in c, f, i) whole‐heart MRI. Quantified CNRblood‐myo significantly improved with the proposed T2Prep‐IR BOOST approach in comparison to the conventional CMRA, thus leading to a higher quantified coronary percentage vessel sharpness (%VS) for both right and left coronary arteries. In the PSIR BOOST images in (c, f, i), the efficacy of blood signal suppression can be appreciated along multiple portions of the coronary tree. BOOST, Bright‐blood and black‐blOOd phase SensiTive; CMRA, conventional coronary MR angiography; IR, inversion recovery; myo, myo, myocardium; PSIR, phase‐sensitive inversion recovery; T2Prep, T2 prepared.
