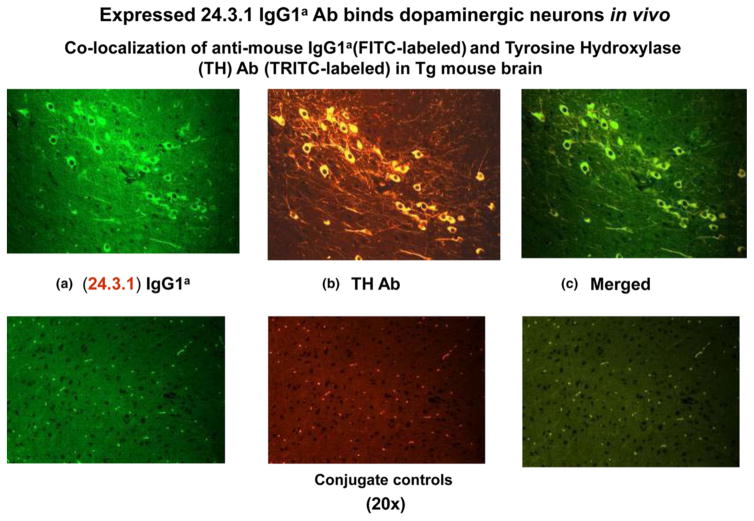
Figure 1.
Human Sydenham chorea 24.3.1 V gene expressed as human V gene-mouse. IgG1a constant region in transgenic (Tg) mice targets dopaminergic neurons. Chimeric Tg24.3.1 VH IgG1a Ab expressed in Tg mouse sera penetrated dopaminergic neurons in Tg mouse brain in vivo. Colocalization of Tg 24.3.1 IgG1a (anti-IgG1a Ab, green, left panel) and tyrosine hydroxylase antibody (anti-TH Ab, yellow, middle panel). TH is a marker for dopaminergic neurons. Left panel shows IgG1a (FITClabelled), centre panel shows TH Ab (TRITC-labelled), and right panel is merged image (FITC-TRITC). Brain sections (basal ganglia) of VH24.3.1 Tg mouse (original magnification 320), showing FITC-labeled anti-mouse IgG1a (a), TRITC-labelled anti-TH Ab (b) and merged image (c). Colocalization by double immunostaining used Abs conjugated to FITC and TRITC. For localization of chimeric Tg24.3.1 VH IgG1a, primary Ab was biotin-conjugated mouse anti-mouse IgG1a (BD Pharmingen) which was used in combination with FITC-conjugated streptavidin (Invitrogen). For immunostaining of dopaminergic neurons, rabbit polyclonal Ab (Abcam) was used as primary Ab with TRITC-conjugated sheep anti-rabbit Ab as the secondary Ab (Sigma). Conjugate controls, secondary Ab controls (secondary Ab, no primary Ab) shown: FITC-conjugated streptavidin (1 : 20) (left panel) and TRITC-conjugated sheep anti-rabbit Ab (1 : 100) (middle panel); right panel is merged image (FITC-TRITC) (Cox et al. 2013).