Figure 2. Potential pathways of NAFLD and NASH development and therapeutic targets for NAFLD/NASH treatment.
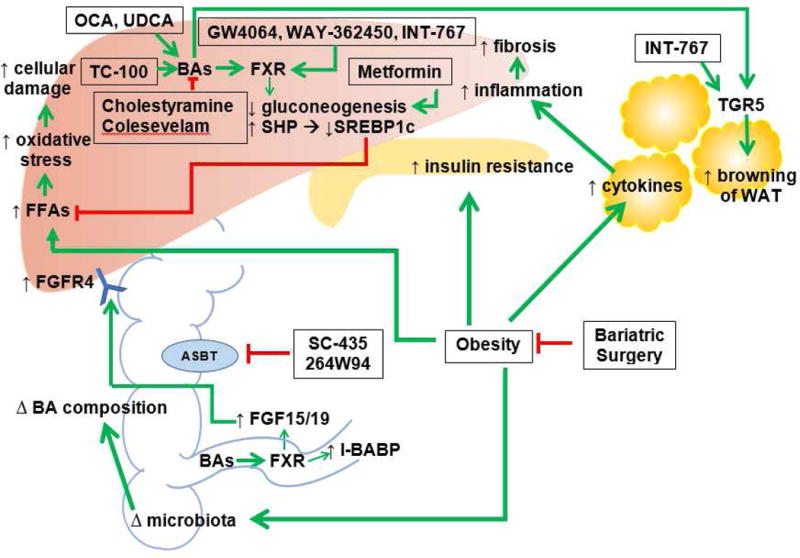
The exact mechanism for NAFLD development and progression to NASH is unknown. However, obesity and insulin resistance/diabetes are believed to be two significant contributing factors. Obesity leads to increased hepatic lipids, insulin resistance, cytokines in WAT, and changes in intestinal flora. Increased hepatic lipids results in increased oxidative stress and apoptosis. Insulin resistance can result in diabetes. Cytokines result in increased hepatic inflammation and with repeated insults, can lead to fibrosis. Changes in microbiota can cause changes in BA composition that can disrupt many pathways, since BAs are important regulators of lipid and glucose metabolism. BA conjugates and derivatives (such as OCA, UDCA, and TC-100) decrease hepatic gluconeogenesis and hepatic lipids. BA conjugates and derivatives can increase hepatic and intestinal FXR. Increased intestinal FXR can lead to increased FGF15/19 and increased FGFR4. BA binding resins (such as cholestyramine and colesevelam), are medications being used by patients with diabetes and despite having an opposite effect on BAs compared to BA conjugates, have been shown to help lower systemic lipids. However, they do not currently have a role in improving hepatic steatosis. Metformin, also used in patients with diabetes, decreases gluconeogenesis. FXR and TGR5 agonists have shown promising results with improvement in glucose tolerance and decrease in hepatic inflammation. ASBT inhibitors (such as SC-435 and 264W94) also show promising results, with decreased expression of SREBP1c and increased FXR (not depicted). Hepatic steatosis and glucose intolerance were demonstrated to be improved in rodent studies using ASBT inhibitors. Finally, bariatric surgery is emerging as another potential therapy for NAFLD and NASH. Bariatric surgery not only leads to weight loss, but has been shown to affect microbiota and improve insulin resistance independent of weight loss (not depicted).
