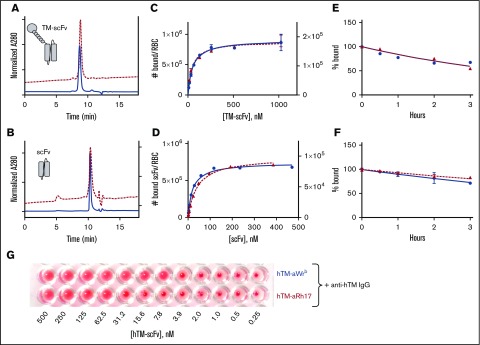
Figure 1.
Characterization of aRh17 and aWrb ligands and their binding to human RBCs. Representative size-exclusion HPLC analysis of (A) hTM-scFv fusions and (B) scFvs alone directed to band 3/GPA (aWrb, solid blue lines) and RhCE (aRh17, dashed red lines) demonstrates high purity of recombinant proteins and elution times consistent with theoretical molecular weights. Direct binding assays with radiolabeled proteins demonstrates high affinity and Bmax (supplemental Table 1) consistent with reported copy number of the surface targets for both the (C) hTM-scFv fusions and the (D) scFv antibodies. No significant nonspecific binding to control murine RBCs was seen. Representative data of 3 independent experiments are shown. Ligand dissociation studies demonstrated slow dissociation kinetics (>50% bound at 3 hours) for both the (E) TM-scFv fusions and (F) scFv antibodies. (G) Binding assay by hemagglutination techniques demonstrated that when anti-hTM IgG antibody (100 nM) was added to RBC prebound with the indicated concentration of hTM-scFv fusions, agglutination was observed when ∼1000 copies of hTM would be expected on the surface. Representative data of 3 independent experiments are shown. No agglutination was seen with RBCs treated with either scFv or hTM-scFv alone or with mouse, rat, or pig RBCs treated with scFv or hTM-scFv followed by anti-hTM.