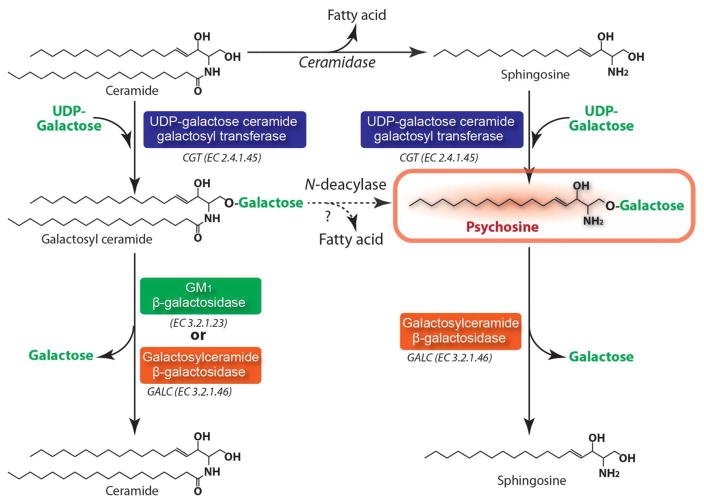
Figure 1. Anabolic and catabolic pathways of psychosine and galactosylceramide.
Galctosylceramide is one of major glycosphingolipids of myelin. It is synthesized by galactosylation of ceramide by the action of UDP-galactose ceramide galactosyl transferase (CGT). Galactosylceramide is degraded to ceramide by degalactosylation by both GM1 β-galactosidase and galactosylceramide β-galactosidase (GALC). Psychosine is synthesized by galactosylation of sphingosine which is generated from deacylation of ceramide by ceramidase. Alternatively, psychosine may also be synthesized from galctosylceramide by the action of N-deacylase. Psychosine is a neurotoxic lysolipid and present at extremely low levels in the cells and tissues under normal conditions. However, under the GALC deficient conditions, PSY accumulates to high levels in tissues, especially in the brain. Unlike most other lysosomal diseases, the primary substrate of GALC (galctosylceramide) is not found at such high levels in Krabbe disease tissues due to its alternative hydrolysis by GM1 ganglioside β-galactosidase.