Fig. 1. C-TSHR-mAb stimulates biased signaling in thyrocytes through the activation of GRK2 and β-arrestin-1.
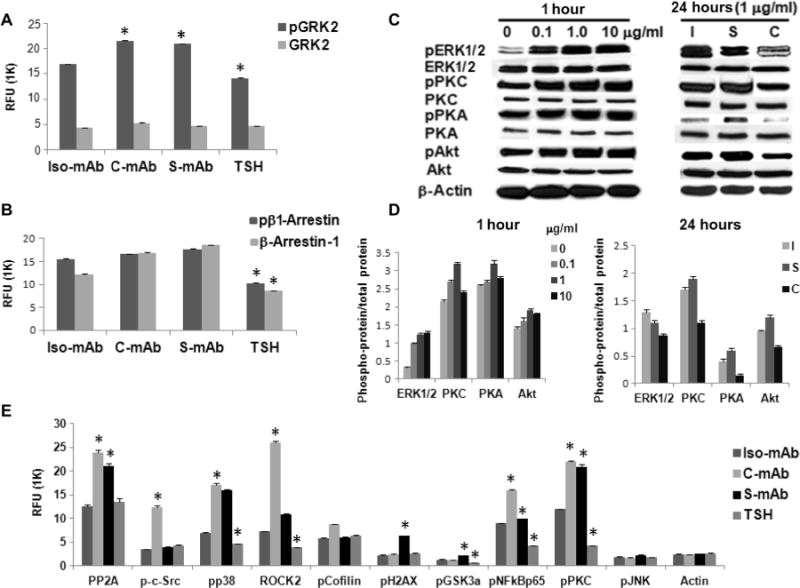
(A) Thyrocytes were treated with thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) (1 mU/ml) or with isotype control monoclonal antibody (Iso-mAb), C-TSHR-mAb (C-mAb), or S-TSHR-mAb (S-mAb) (all at 1 μg/ml) for 1 hour. The relative abundances of total heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide–binding protein (G protein)–coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) and phosphorylated GRK2 (pGRK2) were then measured by proteomic array. The relative fluorescence unit (RFU) from bound antibody was then measured. Data are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.02 compared to isotype control mAb–treated cells. (B) Cells treated as described in (A) were analyzed to determine the relative amounts of total and phosphorylated β-arrestin-1 (pβ1-Arrestin). Data are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.006 compared to isotype control mAb–treated cells. (C) Thyrocytes were treated for 1 hour with the indicated concentrations of C-TSHR-mAb in a dose-dependent manner (left) or for 24 hours (right) compared with isotype control mAb (I) and S-TSHR-mAb (S) (all at 1 μg/ml) before being analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Western blots are representative of three experiments. (D) Densitometric quantification of the Western blots shown in (C). Data are presented as the ratio between the abundances of the indicated total proteins and phosphorylated proteins. β-Actin was used as a loading control. *P < 0.05 compared to untreated or isotype control mAb. (E) Thyrocytes were treated with TSH (1 mU/ml) or with isotype control mAb, C-TSHR-mAb, or S-TSHR-mAb (all at 1 μg/ml) for 1 hour. PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; pp38, phosphorylated p38; pCofilin; phosphorylated cofilin; pH2AX, phosphorylated histone 2AX; pGSK3a, phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase 3α; pNFkBp65, phosphorylated NF-κB p65; pJNK, phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase. The relative abundances of the indicated proteins were then determined by protein array. Data are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared to isotype control mAb–treated cells.
