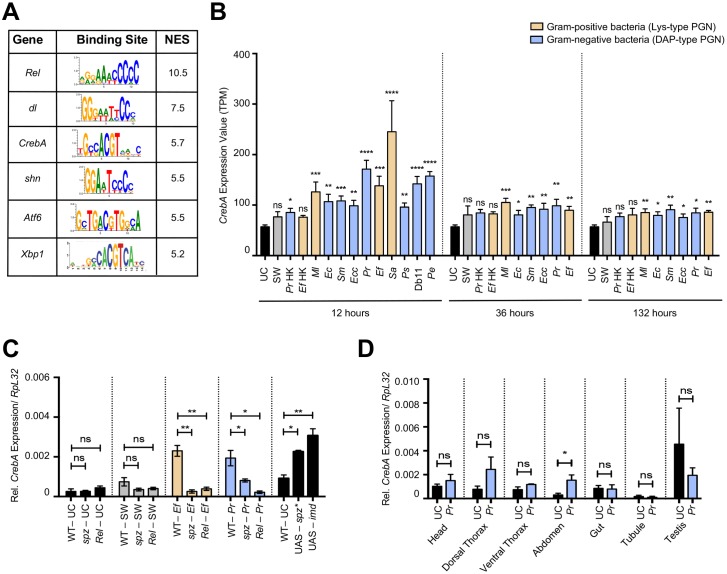
Fig 5. CrebA is a core transcription factor regulated by Toll and Imd in the fat body.
(A) Subset of transcription factors whose predicted binding sites are enriched in the promoter regions of core upregulated genes. The table includes the transcription factors’ gene symbols, consensus binding sites, and their normalized enrichment scores (NES), which indicate the degree to which a binding site is overrepresented at the top of a ranked list of binding sites. (B) RNA-seq expression values in TPM (transcripts per million) of CrebA at 12, 36, and 132 h after infection with all 10 bacteria. (C) RT-qPCR of CrebA levels in RelE20 and spzrm7 mutants and wildtype flies following: no challenge (UC), sterile wound (SW), infection with E. faecalis (Ef), and infection with P. rettgeri (Pr). In the last histogram, WT indicates wildtype flies given no challenge, UAS-spz* denotes CrebA expression in the absence of challenge when an activated form of Spz is ubiquitously overexpressed, and UAS-imd shows CrebA expression in flies that constitutively overexpress Imd in the absence of challenge. (D) RT-qPCR of CrebA levels in dissected organs and body parts (head, dorsal thorax, ventral thorax, abdomen, gut, Malpighian tubule, and testis) following infection with P. rettgeri. Mean values of at least three biological replicates are represented ±SE. *p<0.05 **p<0.01 ***p<0.001 ****p<0.0001 in a Student’s t-test.