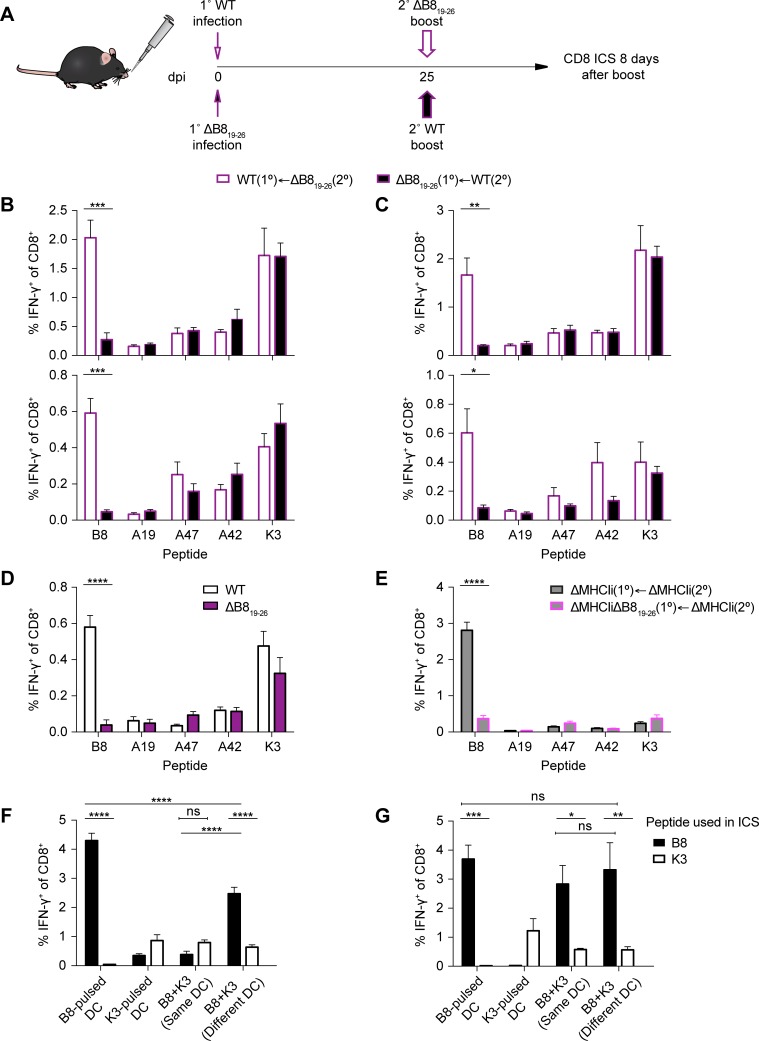
Fig 5. CPXV subdominant epitope-specific memory CTLs immunodominate responses by naïve CD8+ T cells.
(A) Schematic of i.n. prime/boost experiment. (B and C) Immunodomination of naïve CD8+ T cells. B6 mice (n = 5–6) were primed i.n. with 5 x 103 pfu, i.n. boosted at 25 dpi with 5 x 103 pfu (B) or 5 x 104 pfu (C), and sacrificed 8 days after boosting. CD8+ T cell responses in the lungs (top) and spleens (bottom) were determined by ICS. Data are the combined results from two independent experiments. (D) Generation of memory CD8+ T cells. i.n. primed mice were sacrificed at 25 dpi and memory CD8+ T cells were measured in the spleen by ICS. (E) Antibody-independent memory CTL immunodomination. μmT mice were primed by s.s. with 1 x 105 and i.n. boosted with 1 x 105 pfu at 25 dpi. CD8+ T cell responses in the spleens were determined 7 days after boost. Data are the combined results from two independent experiments. (F) Memory CTLs cross-compete for peptide-MHCI complexes on APCs. Peptide-pulsed BMDCs were adoptively transferred by tail vein injection into ΔB819-26-primed B6 mice (n = 4) and CD8+ T cell responses in the spleen were evaluated by ICS 6 days after transfer. (G) Naïve CD8+ T cells do not cross-compete for peptide-MHCI complexes on APCs. Peptide-pulsed BMDCs were transferred into naïve B6 mice and CD8+ T cell responses were evaluated by ICS as in the experimental setup of F. Data are representative of two independent experiments.