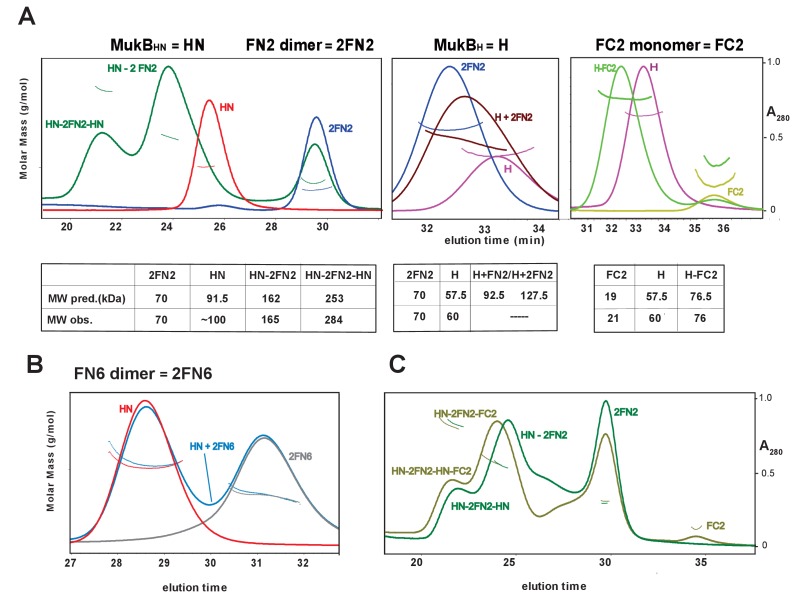
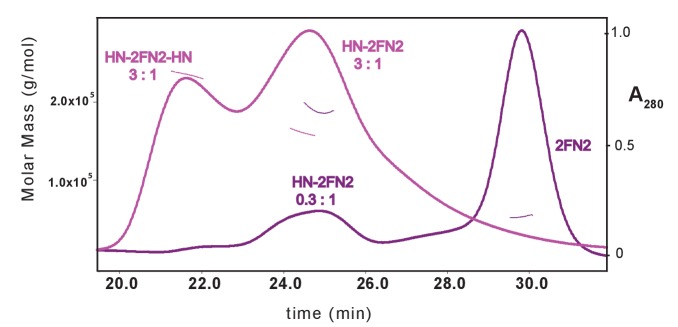
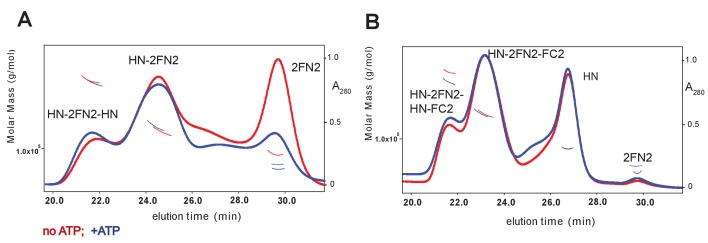
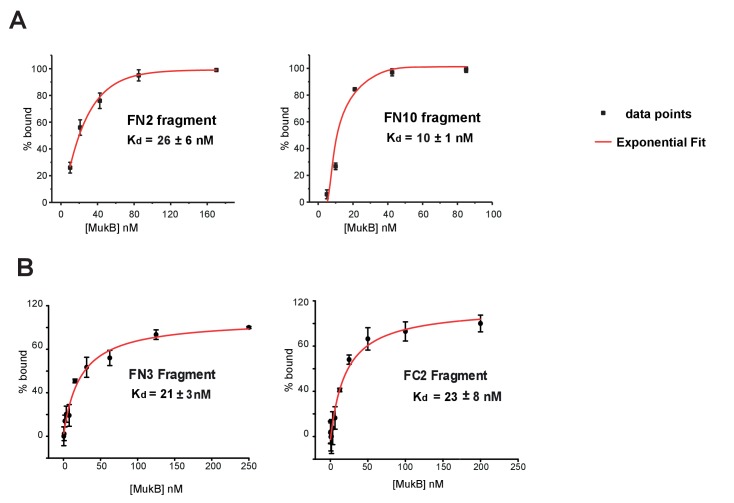
Figure 3. Complexes of MukF N- and C-terminal domains with MukB head variants.
Binding and stoichiometry of complexes was determined by SEC-MALS. (A) Left panel; MukBHN (red), 2FN2 (blue), and MukBHN + 2FN2 (green) at a 1:1.25 monomer:dimer molar ratio. Middle panel; MukBH (pink), 2FN2 (blue), and MukBH + 2FN2 (brown) at 1:0.25 m:d ratio. Right panel; MukBH (pink), FC2 (lime green), and MukBH + FC2 (green) at a 1:1 m:m ratio. (B) MukBHN (red), 2FN6 (grey), and MukBHN + 2FN6 (blue) at a 1:0.25 m:d ratio. (C) MukBHN + 2FN2 at a1:1 m:d ratio (dark green), and MukBHN + 2FN2 + FC2 at a 1:1:1 m:d:m ratio (olive green).