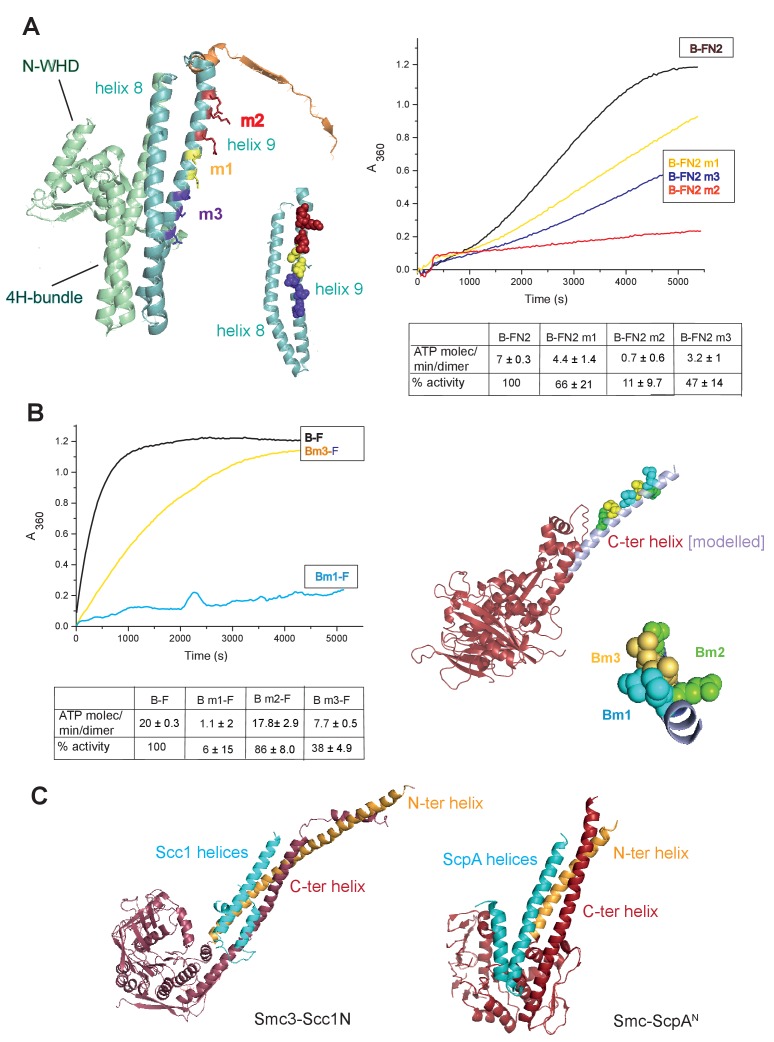
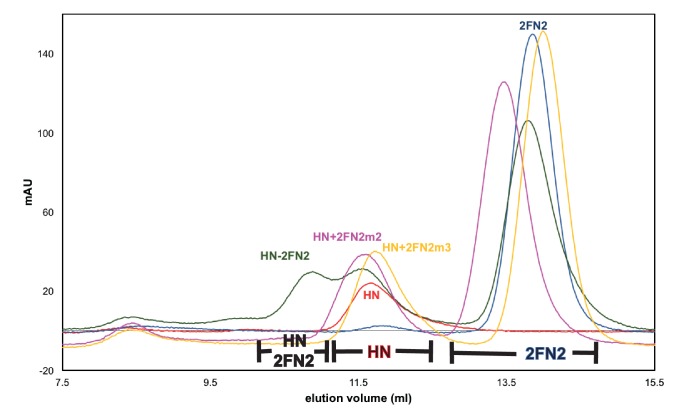
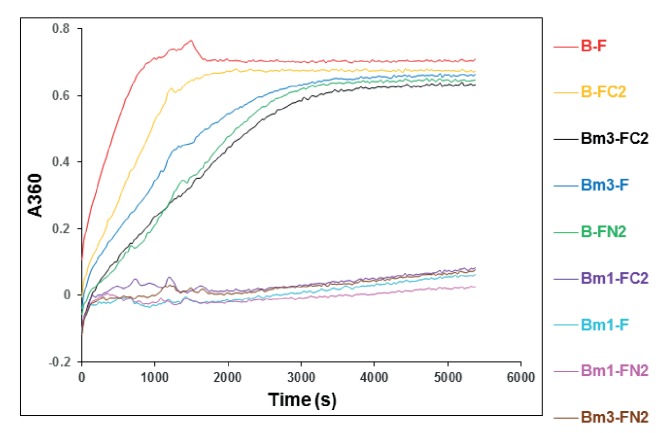
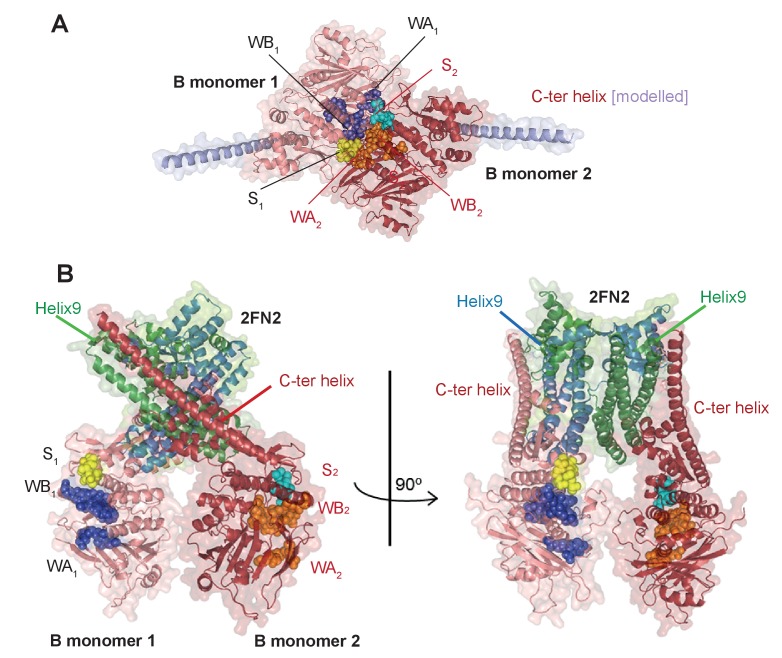
Figure 5. Interface between the MukB neck and the MukF four-helix bundle.
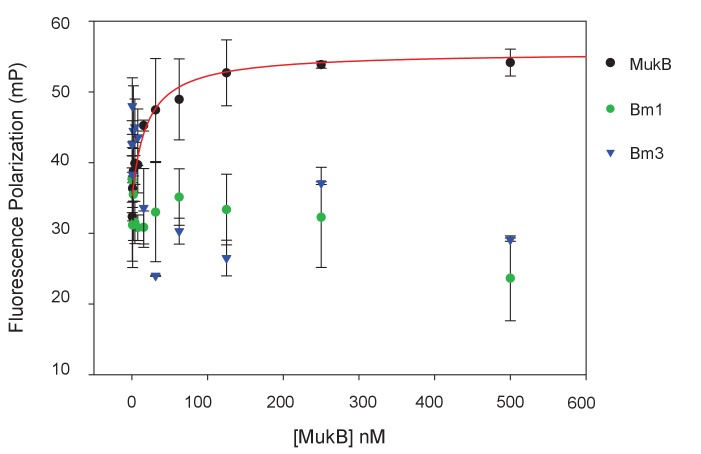
(A) Left panel; cartoon of MukF N-terminal domain fragment carrying the N-terminal dimerisation domain (green) and part of the middle region (orange). Helices 8 and 9 are indicated in cyan. The mutated amino acid residues in variants FN2m1, FN2m2 and FN2m3 are indicated in yellow, red and purple, respectively, (residue R279 was altered in both m1 and m2, but is shown only in m2); views of helices 8 and 9 from different angles are shown separately. Right panel; ATPase activities of the mutated variants; means of initial rate measurements from three experiments are tabulated below. (B) Left panel; ATPase activities in the presence of MukF, of MukB and MukB variants mutated at the neck, MukBm1, blue, and MukBm3, yellow. Averages of initial rates from three experiments are tabulated underneath. Right panel; monomer of the MukB head (pdb 3EUK, Woo et al., 2009); the helix that emerges from the C-terminal subdomain of the head (C-ter helix) and forms the head-adjacent segment of the coiled-coil has been extended by modelling (shown in lilac). Right; enlarged view of the C-ter neck helix from the top with mutated residues shown. (C) Interactions of kleisin N-terminal domains with SMC necks. Left panel; Smc3-Scc1N; Gligoris et al. (2014). Right panel; B. subtilis SMC-ScpAN; Bürmann et al. (2013). The coiled-coil neck consists of two helical regions protruding from the SMC N-terminal head subdomain (N-ter helix; yellow), and from the C-terminal head subdomain (C-ter helix; red). Kleisin helices are shown in cyan.