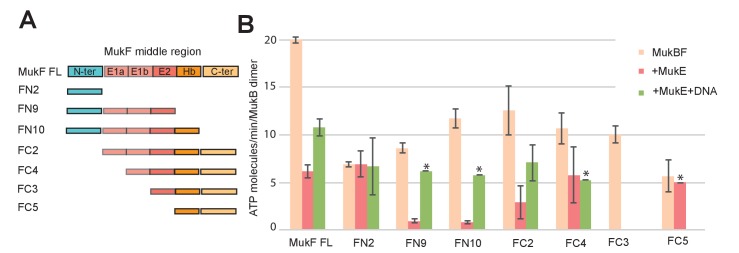
Figure 7. Influence of the MukF middle region on the modulation of MukB ATPase by MukE and DNA.
(A) One monomer of a MukE dimer binds helical region E1a and part of the acidic linker E1b, while the second MukE monomer binds E2. Hence, MukE binds FC2, containing the entire middle region, but not FN2, which lacks the middle region (Figure 7—figure supplement 1). The C-terminal part of the MukF middle region forms an extended polypeptide that binds the MukB head in the asymmetric complex (Hb; Woo et al., 2009). (B) Stimulation of MukB ATPase by MukF variants in the presence and absence of MukE and DNA (53nt ds fragment at 10-fold molar excess over MukB). The bars show means of the initial rates ± SD from three independent experiments.