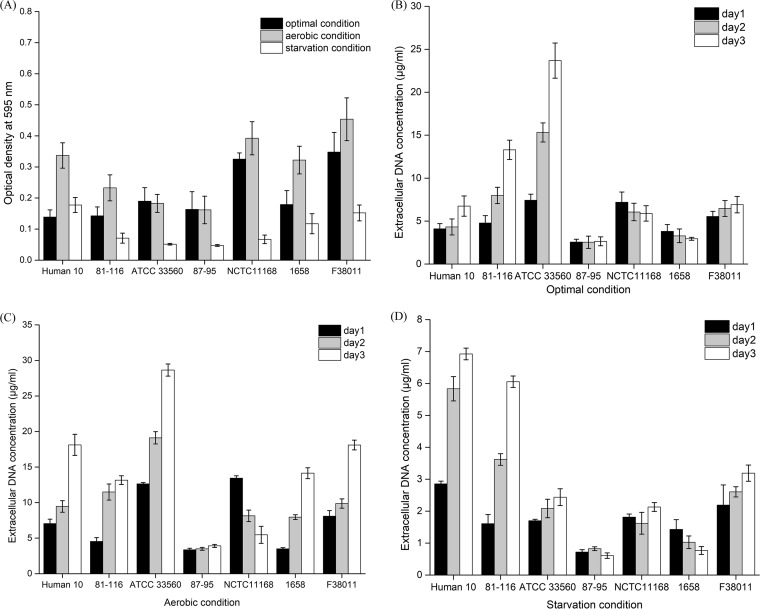
FIG 1.
Biofilm formation and release of extracellular DNA (eDNA) by wild-type C. jejuni strains (i.e., human 10, 81-116, ATCC 33560, 87-95, NCTC 11168, 1658, and F38011) under optimal, aerobic, and starvation conditions. (A) The level of biofilm formation was evaluated using crystal violet staining. The stained biofilm was released using 95% ethanol and determined by monitoring the value of OD595. (B to D) The concentration of eDNA during biofilm formation under optimal conditions (B), aerobic conditions (C), and starvation conditions (D) over 3 days was quantified using SYBR green I dye on the basis of a standard curve generated using a series of 10-fold dilutions of Lambda DNA from 80 μg/ml to 0.156 μg/ml.