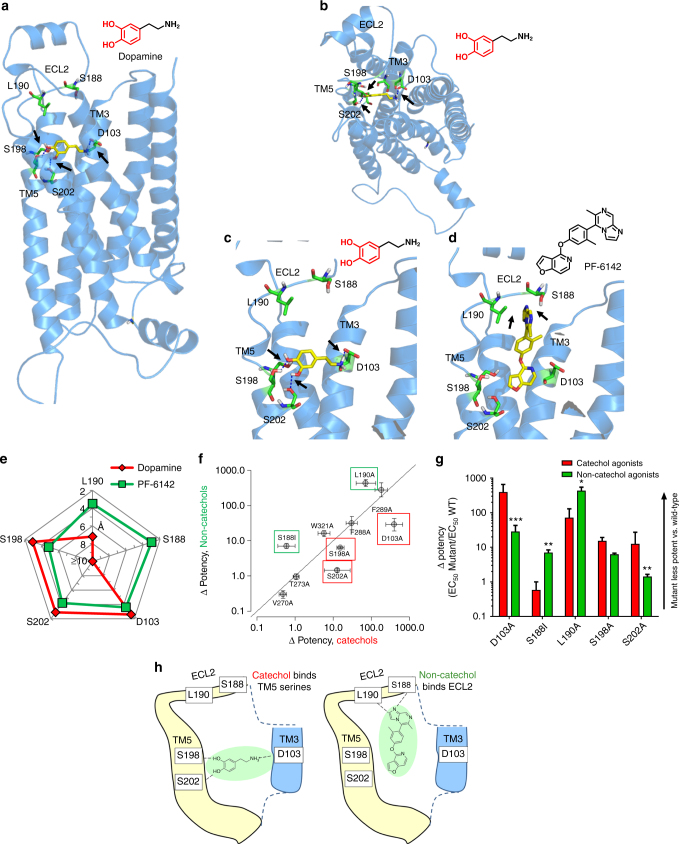
Fig. 3.
Non-catechol D1R agonists adopt a unique binding mode contacting ECL2. a–e Structural homology ligand docking models of the human D1R were simulated using the agonist bound crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor. a–c Docking models of dopamine bound to the D1R in the orthosteric binding site show catechol hydroxyls making hydrogen bond polar interactions with serines 198 and 202 (S198, S202) on transmembrane helix 5 (TM5) and the amine group forming a salt bridge ionic interaction with glutamate 103 (D103) on helix 3 (TM3). d Non-catechol agonist PF-6142 modeled in the orthosteric site and extended D1R binding pocket and making notable contacts with residues in extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) including serine 188 (S188) and leucine 190 (L190). e Molecular docking computations showing the nearest atomic distance (in Å) between dopamine or PF-6142 and key amino acid residues in the D1R orthosteric and extended sites as a spider plot. PF-6142 displayed close atomic juxtaposition to S188 and L190 within ECL2 and more distant positioning relative to residues in TM5. f Correlation plot of catechol and non-catechol agonist potency shifts in functional assay (Δpotency = D1 cAMP EC50mut/D1 cAMP EC50wt) caused by mutation of individual D1R residues. Mutation of ECL2 residues S188A and L190A (green boxes) resulted in larger Δpotency for non-catechol agonists while mutation of TM5 S198A or S202A and TM3 D103A (red boxes) selectively reduced catechol agonist potency. g Change in potency of catechol or non-catechol agonist-induced cAMP signaling following mutation of critical residues identified by docking models. Data are presented as Δpotency on a log scale defined as the potency means ± s.e.m. of mutant/wild type receptor. Two-way ANOVA revealed significant effects of mutant (F(4,34) = 29.7, P < 0001 and interaction between mutant and compound type (F(4,34) = 14.7, P < 0001, non-significant effect of compound type (F(1,34) = 2.9, P < 0.1, post-hoc tests indicated significantly higher Δpotency in catechol group for D103A, S202A (***P < 0.001) and lower Δpotency in catechol group for S188I (***P < 0.001) and L190A (*P < 0.05). h Schematic model of dopamine or PF-6142 differentially binding to TM5, TM3, and ECL2 residues surrounding the D1R orthosteric ligand binding site