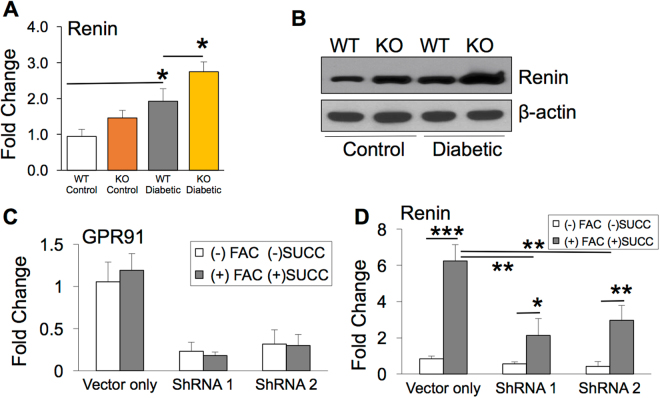
Figure 6.
Iron overload during diabetic retinopathy upregulates retinal renin expression in a GPR91 dependent mechanism. (A) Pro/renin mRNA quantified in retina of non-diabetic and diabetic HFE WT and HFE KO mice by RT PCR (B) Renin protein levels quantified in retina of non-diabetic and diabetic HFE WT and HFE KO mice by western blot. Blots cropped from different parts of the same gel or from different gels are separated by white space. (C) Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of GPR91 expression in ARPE-19 cells treated with two different GPR91-specific shRNAs34. GPR91 knockdown was quantified by RT-PCR with 18S RNA as an internal control. Control ARPE-19 cells (vector only) and GPR91 shRNA-expressing ARPE-19 cells were treated with 100 μg/mL FAC for 72 hours, and during the last 16 hours of this 72-hour FAC treatment, cells were incubated with or without 2 mM succinate. (D) Renin mRNA levels were analyzed using RT-PCR in RNA from control ARPE-19 cells (vector only) and GPR91 shRNA-expressing ARPE-19 cells with or without the treatment of FAC and succinate. 18S RNA was used as an internal control. Data presented as mean ± SE of three experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001.