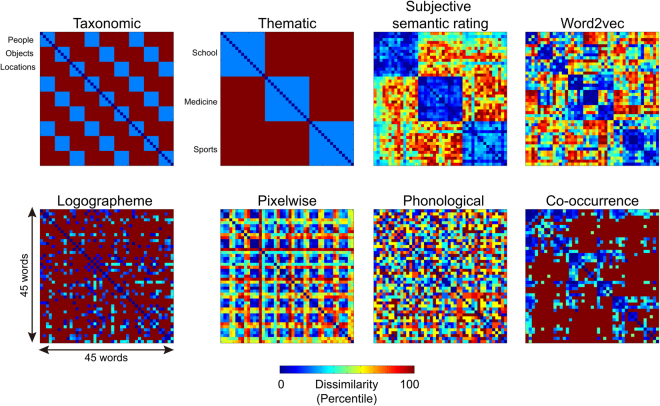
Figure 1.
Theoretical/behavioral representational dissimilarity matrices. The binary taxonomic and thematic RDMs illustrated the membership of each word in three taxonomic categories (people, objects, and locations) and three thematic categories (school, medicine, and sports). The subjective semantic rating RDM was based on explicit ratings of semantic distance. The word2vec RDM was calculated as the cosine distance of vector representations of words learned in a skip-gram model. The logographeme, pixelwise and phonological RDMs were constructed by one minus the proportion of shared logographemes, overlapping pixels for visual words in a pictorial format and shared sub-syllabic units and tones, respectively, for a given word pair. The co-occurrence RDM was constructed based on the summed counts of co-occurrence within a window of five words for a given word pair in a language corpus.