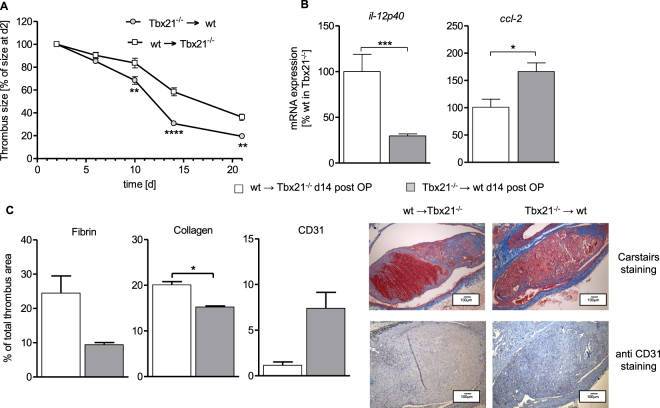
Figure 5.
Critical role of T-bet in bone marrow-derived cells for thrombus resolution. (A) Thrombus sizes determined by high frequency ultrasound calculated as percentage at day 2, of thrombi in irradiated C57BL/6 wild type mice (CD45.1+ Ly5.1) mice transplanted with bone marrow of Tbx21−/− mice (Tbx21−/− → wt) compared to irradiated Tbx21−/− mice transplanted with wild type bone marrow (wt→ Tbx21−/− mice) at indicated time points following IVC stenosis. Mean ± SEM; two-way ANOVA/Bonferroni post hoc test; n = 3–4; **p ≤ 0.01; ****p ≤ 0.0001. (B) Analysis of il-12p40 and ccl-2 mRNA expression in thrombus material. Mean ± SEM. n = 3–4 animals per group; t-test; *p ≤ 0.05. (C) Histological staining (Carstairs staining) and immunohistochemistry (CD31 staining) of IVCs 14d after subtotal ligation. Magnification x10. Summary of the quantitative analysis, results in mean ± SEM. n = 3–4 animals per group; t-test; *p ≤ 0.05.