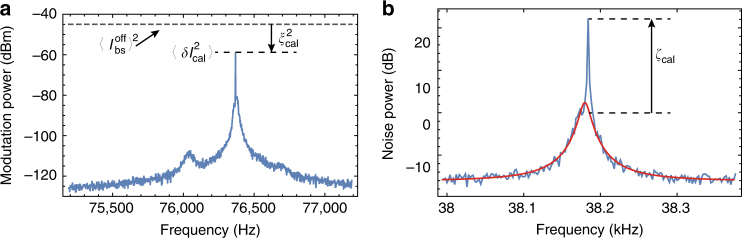
Fig. 4.
Calibration of the nanomechanical motion. a Spectrum of the optomechanical response acquired at the centre of the beam waist. The nanomechanical motion is piezo-driven resonantly, resulting in a sharp peak at twice the mechanical resonance frequency. This peak sits on a large noise pedestal resulting from the quadratic optomechanical transduction of the Brownian motion. ( here) is the ratio between the (DC) power level of the reflected light in absence of any piezo excitation (dashed line) and the driven peak at 2Ωm. b Spectrum of the optomechanical response acquired on the side of the beam waist (straight blue line), where linear optomechanical transduction is non zero. The straight, red line corresponds to the Lorentzian fit of associated to thermal noise. ζcal (, grossly) corresponds to the ratio between the driven peak (upper dashed line) and the thermal noise level (lower dashed line)