Figure 1.
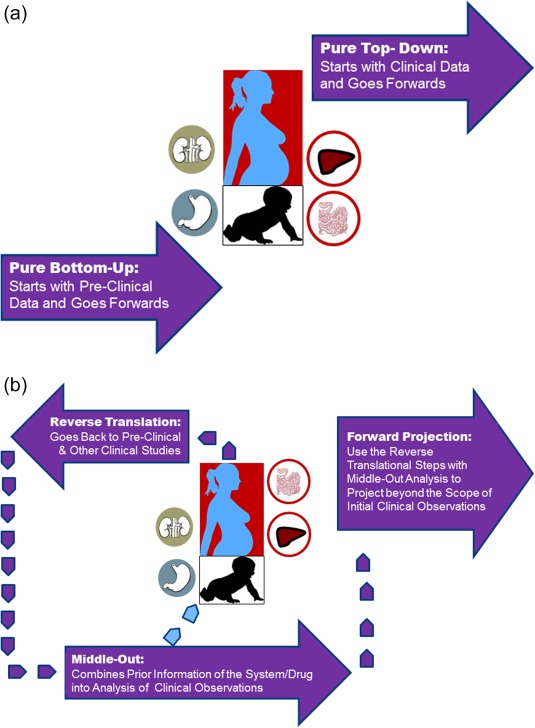
(a,b) The schematics of the differences between purely bottom‐up and pure top‐down approaches (a), vs. the combined models (b). For combined approach, in recent years we have witnessed many PBPK‐IVIVE approaches that are built based on preclinical data and then complemented by a designed study to qualify the model (Index Study, as it is called in the latest FDA Guidance). However, if for any reason such models are not built, it is still possible to do a “reverse translation” by taking observed clinical data and building a model that takes into account all prior knowledge about that drug and the systems information. In reality, the loop between clinical observations and preclinical data might be reiterated several times before a projection is made for cases which are not studied for a variety of ethical and practical reasons such as conducting drug–drug interaction studies in neonates, renal or hepatic impairment, pregnancy, the elderly, and so on; even the vulnerability of these patients could be very different from those of healthy volunteer populations.
