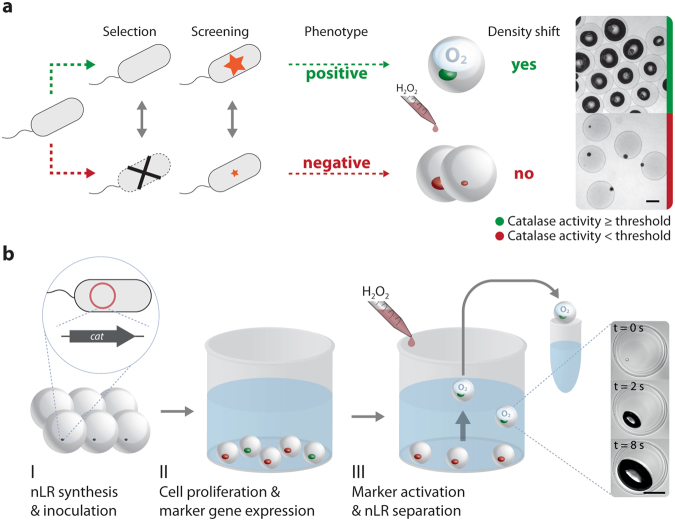
Figure 1.
High-throughput phenotyping of whole cell biocatalysts employing buoyancy modulation markers. (a) Assays based on selection or on screening can be adapted to buoyancy separation. In both cases, the amount of catalase marker in an nLR needs to become larger than a critical threshold in order to make an nLR (and the strain variant residing within) ascend. This can be achieved by varying the biomass level (selection scenario) or the expression level (screening scenario). Scale bar: 200 µm. (b) Separation workflow. (I) Single library cells are encapsulated into nLRs. (II) The nLRs are incubated in growth medium until microcolonies are formed. (III) H2O2 is added and microcolony-containing nLRs with a catalase amount beyond the threshold ascend within a few seconds due to the formation of an O2-filled gas chamber within their interior (see inset and Supplementary Video 1). Scale bar: 150 µm.