Figure 4. The ERAD‐protein VCP is required for Evi destabilization.
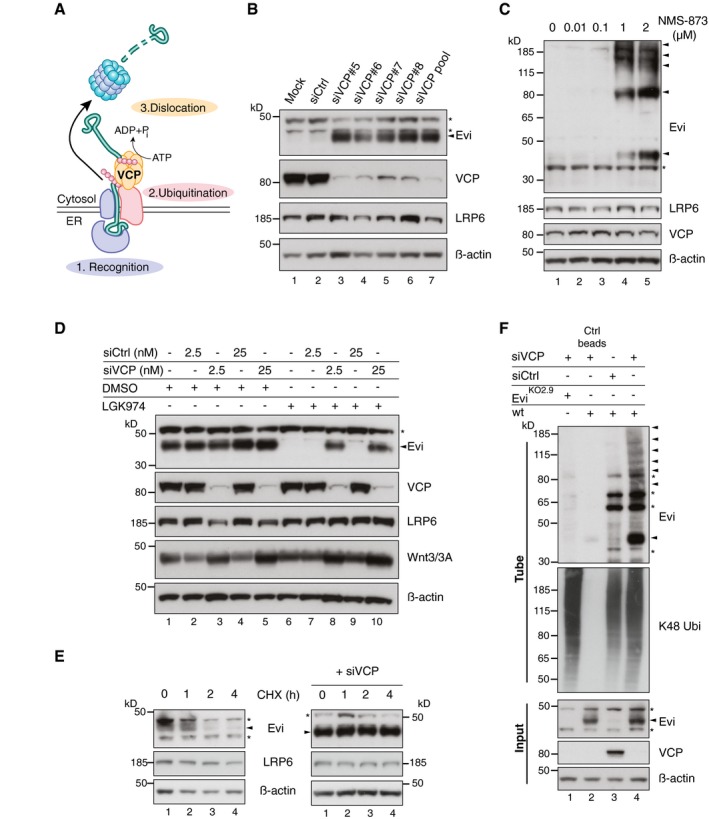
- ERAD‐dependent degradation requires recognition, ubiquitination, and subsequent dislocation of the selected substrates through the ER membrane to cytosolic proteasomes. ATP‐dependent dislocation is mediated through the AAA‐type ATPase VCP.
- Western blot analysis of endogenous Evi and the indicated proteins in HEK293T cells upon knockdown of VCP using single or pooled VCP siRNAs.
- HEK293T cells were treated for 24 h with the VCP inhibitor NMS‐873 at the indicated concentrations and analyzed for the indicated proteins by immunoblotting.
- Following reverse transfection with pooled VCP or Ctrl siRNAs (2.5 nM or 25 nM), stable Wnt3‐expressing HEK293T cells were treated with 5 μM LGK974 or DMSO for 48 h and analyzed for the indicated proteins.
- After reverse transfection with pooled VCP siRNAs (if indicated), HEK293T cells were treated with 50 μM cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated hours (h). Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting.
- EviKO2.9 or wild‐type (wt) HEK293T cells were reverse transfected with pooled VCP or Ctrl siRNAs and analyzed for ubiquitinated Evi and K48 ubiquitinated proteins by TUBE2 precipitation. All Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. β‐Actin was used as a loading control and LRP6 as a reference membrane protein involved in Wnt signaling. Specific Evi bands are indicated by arrows and unspecific bands by asterisks.
Source data are available online for this figure.
