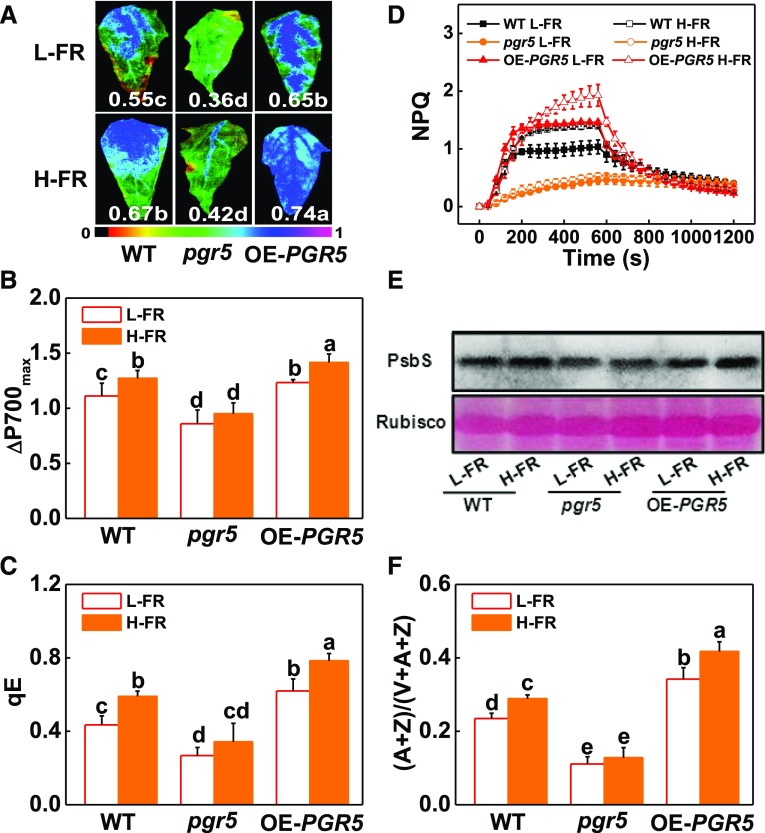
Figure 7.
PGR5-dependent CEF plays dual roles in preventing plants from photoinhibition. A and B, Fv/Fm (A) and ΔP700max (B) of the wild type, pgr5 mutant (pgr5#5), and PGR5-overexpressing (OE-PGR5#3) transgenic plants grown at 4°C under L-FR or H-FR light conditions for 7 d. The false color code depicted at the bottom of the image ranges from 0 (black) to 1.0 (purple) represents the level of damage in leaves. C and D, qE (C) and NPQ (D) in the wild-type, pgr5#5 mutant, and OE-PGR5#3 tomato plants after exposure to 4°C for 3 d under l-FR and H-FR conditions. E and F, PsbS protein (E) and de-epoxidation state of the xanthophyll cycle (F) in the wild-type, pgr5#5 mutant, and OE-PGR5#3 tomato plants after exposure to 4°C for 1 d and 3 d, respectively, under L-FR and H-FR conditions. For the L-FR and H-FR, R/FR values at 1.5 and 0.5, respectively, plants were kept at R conditions (200 μmol m−2 s−1) supplemented with different intensities of FR (133 μmol m−2 s−1 and 400 μmol m−2 s−1). Data are the means (±sd) of four biological replicates, except for Fv/Fm, which are the means for 15 leaves from independent plants. Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to the Tukey’s test. WT, wild type.