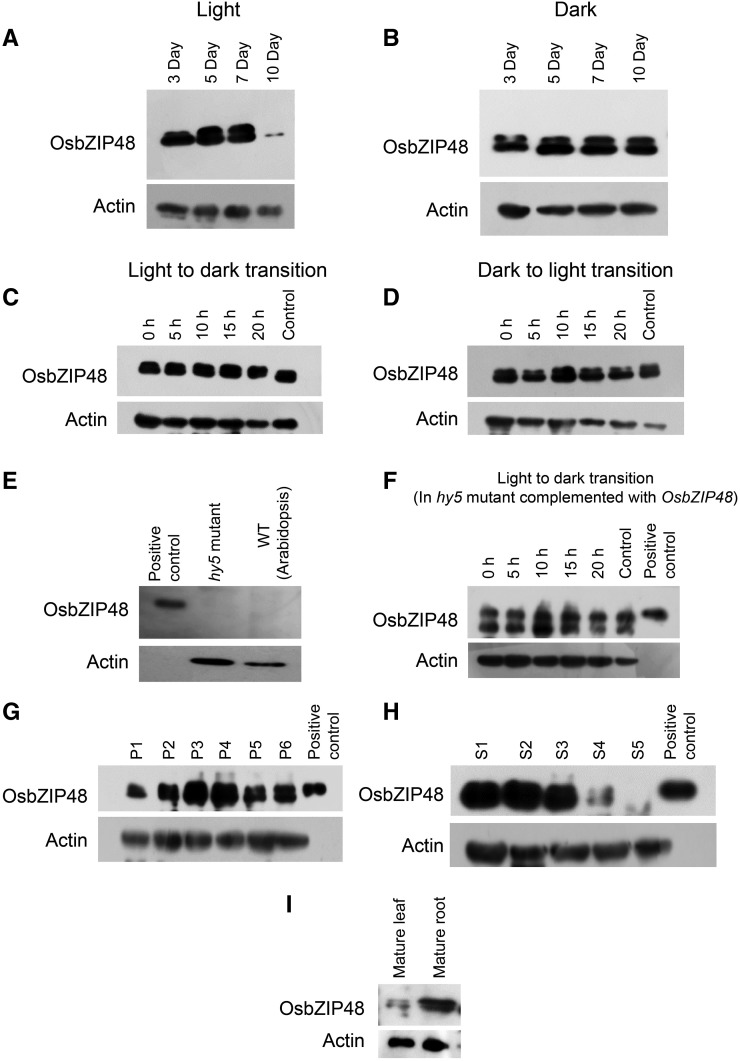
Figure 3.
Western blots showing OsbZIP48 protein expression levels in different tissues of rice and the Arabidopsis hy5 mutant complemented with OsbZIP48. A, OsbZIP48 protein levels in 3-, 5-, 7-, and 10-d-old light-grown rice seedlings (100 μmol m−2 s−1). B, OsbZIP48 protein levels in 3-, 5-, 7-, and 10-d old dark-grown rice seedlings. C, OsbZIP48 protein levels in seedlings grown in continuous light for 4 d and then transferred to dark for 5, 10, 15, and 20 h; the control is 5-d-old seedlings grown in continuous light. D, OsbZIP48 protein levels in seedlings grown in continuous dark for 4 d and then transferred to the light for 5, 10, 15, and 20 h; 5-d-old seedlings grown in continuous dark were used as the control. E, Western blot using OsbZIP48 antibodies shows no cross-reactivity with Athy5 mutant protein extracts. F, OsbZIP48 protein levels in Arabidopsis hy5 mutant seedlings complemented with OsbZIP48, grown in continuous light for 4 d, and then transferred to the dark for 5, 10, 15, and 20 h; control represents 5-d-old seedlings grown in continuous light. G, Changes in OsbZIP48 protein levels during various stages of panicle development in rice. H, OsbZIP48 protein levels during seed development (S1–S5) stages in rice. I, OsbZIP48 protein levels in mature leaf and root in rice. The positive control in E to H is bacterially expressed 6× His-tagged OsbZIP48 protein.