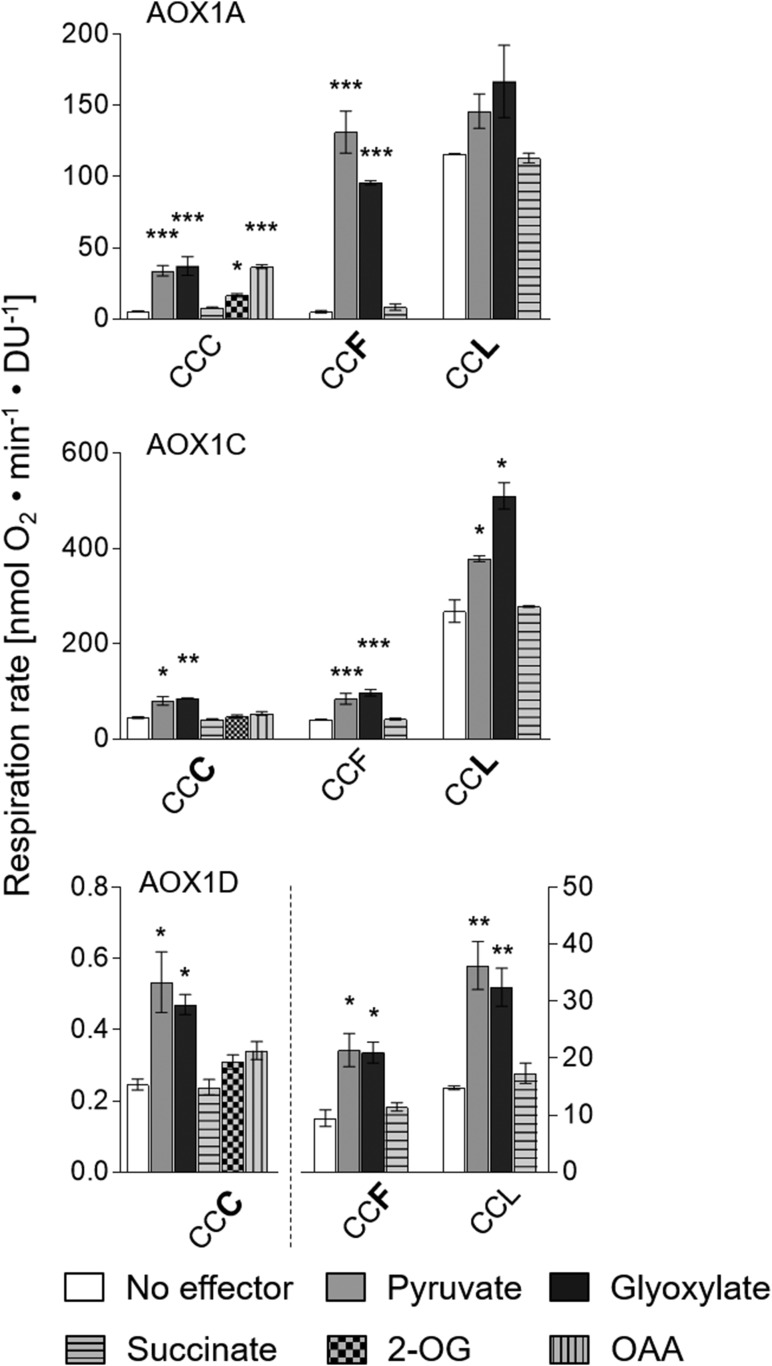
Figure 3.
Convertibility of AOX isoforms into one another by substitutions of amino acid residues at position CysIII. Oxygen consumption measurements and calculations of specific respiration rates (nmol oxygen min−1 density units [DU]−1) were performed as described by Selinski et al. (2016). Measurements were carried out as three independent biological replicates. Each biological replicate was measured twice, leading to a total of six values per column. Basal activities (no effector) were 5.71 ± 0.15 nmol oxygen min−1 DU−1 for AOX1A-WT (CCC), 40.89 ± 0.87 nmol oxygen min−1 DU−1 for AOX1C-WT (CCF), and 14.81 ± 0.34 nmol oxygen min−1 DU−1 for AOX1D-WT (CCL). Asterisks indicate that the differences (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001) between the basal activity (no effector) and activities in the presence of the effectors are statistically significant as determined by two-way ANOVA with posthoc Tukey’s HSD test. Wild types are as follows: AOX1A, CCC; AOX1C, CCF; and AOX1D, CCL. Substitutions are presented in the one-letter code for amino acids in enlarged boldface letters. Note the difference in scale for AOX1D proteins: the left y axis belongs to AOX1D-CCC, and the right y axis belongs to AOX1D-CCF and AOX1D-CCL.