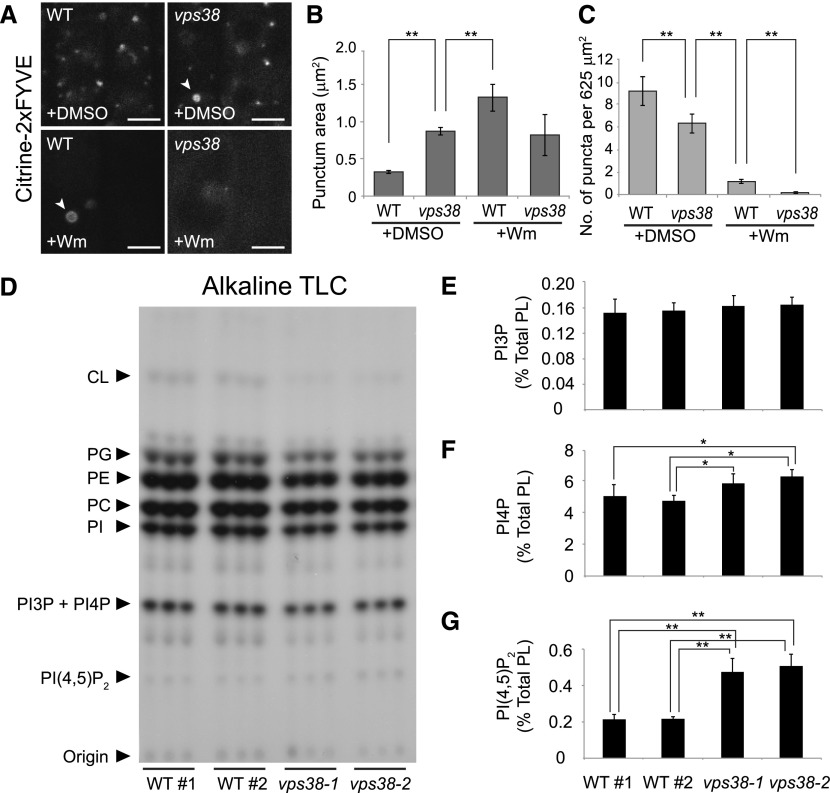
Figure 3.
vps38 affects the intracellular distribution of PI3P but not its total levels. A, Root tip images of wild-type and vps38 expressing the PI3P biosensor, citrine-2xFYVE. Wild-type and vps38 seedlings expressing the sensor were incubated with either 30 μm Wm or DMSO for 1 h before confocal imaging. Arrowheads indicate ring-shaped compartments. Bars = 5 μm. B and C, Graphs illustrate area (B) and density (C) of the citrine-2xFYVE puncta in DMSO- or Wm-treated wild type and vps38-1 (mean ± se; n > 46 regions of interest; *, 0.01 < P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). D, Autoradiograph of TLC of 32P-labeled lipid extracts, which were prepared from three biological replicates, each consisting of three seedlings selected from four seed populations of wild type and two vps38 alleles that were 32Pi-labeled in vivo. E to G, Levels of PI3P (E), PI4P (F), and PI(4,5)P2 (G) were quantified by phosphoimaging the phosphoinositide spots in (D) and determining the ratios of PI3P to PI4P by HPLC analysis (see “Materials and Methods”). Columns (mean ± sd) marked with asterisks represent significantly different means (*, 0.01 < P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). CL, cardiolipin; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PI, phosphatidylinositol; WT, wild type; WT#1 and WT#2, wild-type seed populations.