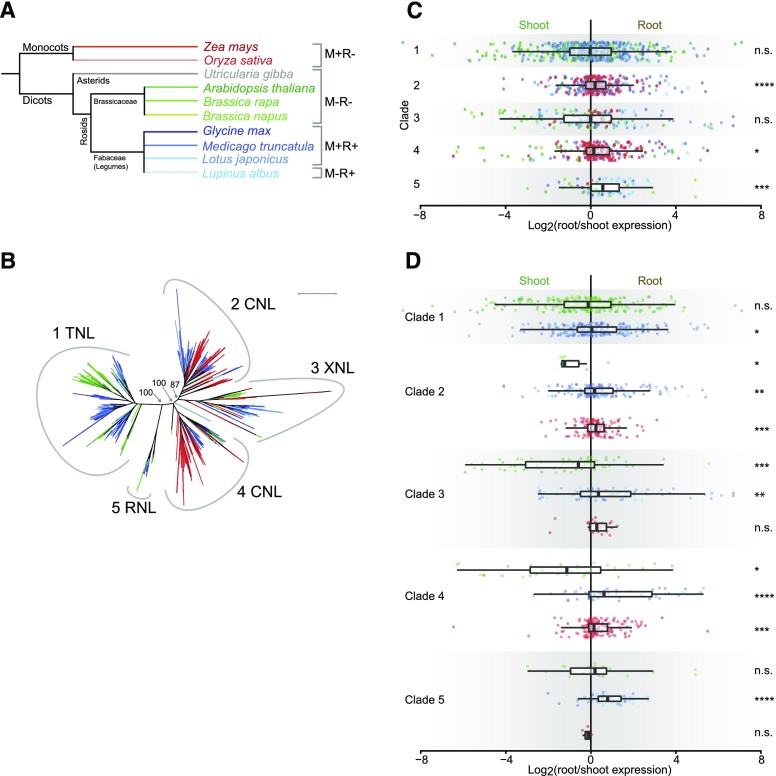
Figure 2.
NLR expression patterns by phylogenic clade. Colors indicate the plant species from which the NLR originates with reference to Figure 2A. A, Species-level phylogenetic tree. The symbiotic status of each species is indicated on the right. M, mycorrhiza; R, rhizobia; +, engages in endosymbiosis; -, does not engage in endosymbiosis. B, Phylogenetic tree based on the NBD protein sequence of identified NLR genes in the species indicated in Figure 2A. Numbers at branches indicate bootstrap values for the branching of the five major clades. Peripheral numbers indicate clade designation, and NLR designation indicate enrichment of the corresponding NLR type in the given clade. Scale bar indicates 1.0 average amino acid substitutions per site. See Supplemental File S2 for full bootstrap analysis of the tree. See Supplemental Table S7 for NLR distribution at the clade and species level. C, Per clade log2 root/shoot expression ratios of the NLR genes shown in B for which expression data are available. Each colored dot represents one NLR gene. Box plot bars show median with boxes indicating 25th and 75th percentiles and whiskers indicating 1.5 times the interquartile range. D, Same as C but with expression data separated into groups depending on the species evolutionary descent colored according to Figure 2A. ****P ≤ 0.0001, ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05. n.s., not significant. Student’s t test was used for calculation of P values. See Supplemental Table S9 for P values for interclade and interspecies differences.