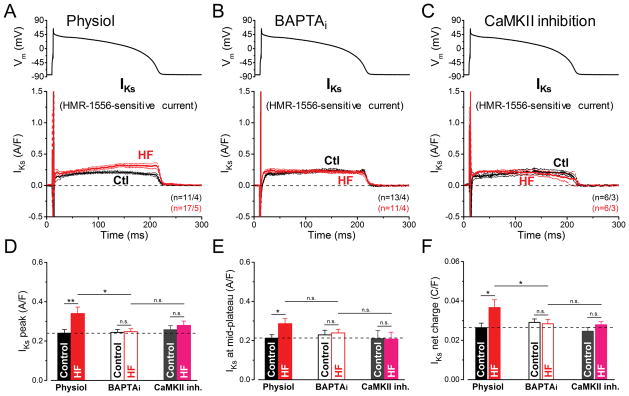
Figure 4. Ca2+/CaMKII-dependent upregulation of IKs in HF under AP-clamp.
The slow component of delayed rectifier K+ current (IKs) was measured as HMR-1556 (1 μM)-sensitive current in HF and age-matched control cells. AP-clamp using a prerecorded typical AP (shown above) was applied at 2 Hz. (A) IKs traces (mean±SEM) recorded under preserved [Ca2+]i cycling (Physiol). Basal IKs is a tiny current under AP, yet it is significantly upregulated in HF cells having [Ca2+]i transients. (B) IKs traces (mean±SEM) recorded under buffered [Ca2+]i using 10 mM BAPTA in the pipette (BAPTAi). Buffering [Ca2+]i reduced IKs in HF back to its control level. (C) IKs traces (mean±SEM) recorded in cells pretreated with the specific CaMKII inhibitor peptide AIP (1 μM). AIP abolished the IKs upregulation in HF. (D) Peak IKs density is significantly upregulated in HF under AP by a Ca2+/CaMKII-dependent pathway. (E) IKs density measured at the mid-plateau of the AP. (F) Net charges carried by IKs in HF and age-matched control. Columns and bars represent mean±SEM. n refers to cells/animals measured in each group. ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest, *p<0.05, **p<0.01.