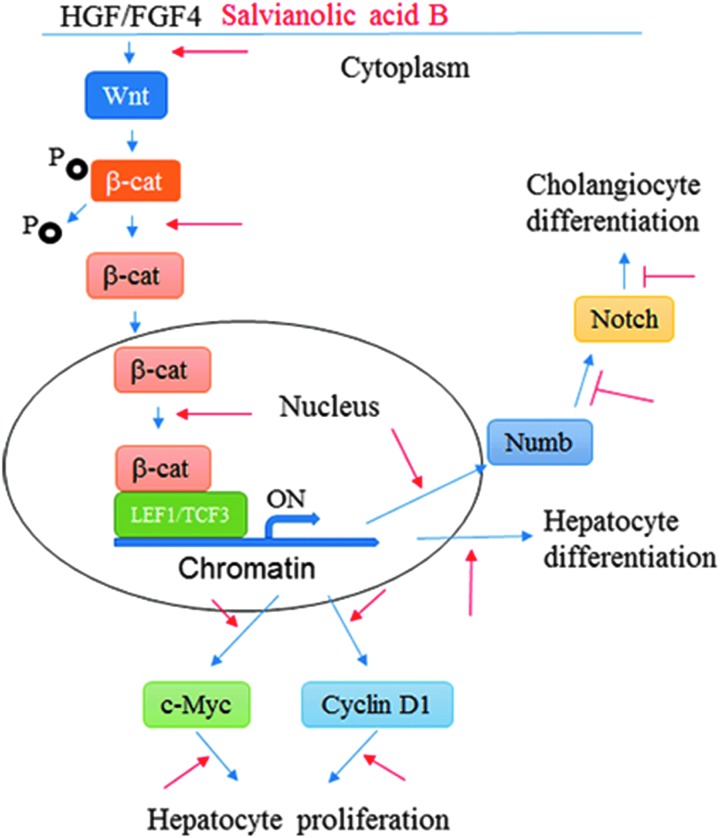
FIG. 7.
Illustration of the effects of Sal B on hepatocyte differentiation from human ESC. Under the culture conditions with HGF and FGF4, the Wnt signaling pathway was activated to regulate hepatocyte differentiation from human ESC. Free β-catenin after dephosphorylation was translocated into the nucleus where β-catenin binds to LEF1/TCF3 to trigger the expressions of the downstream genes, including those that promote hepatocyte differentiation, c-Myc and cyclin D1, which facilitate cell proliferation, as well as Numb, which acts as a negative regulator of the Notch signaling pathway to inhibit cholangiocyte differentiation, is also upregulated. Thus, Sal B treatment upregulates the Wnt signaling pathway (red arrow) to enhance hepatocyte differentiation and downregulates the Notch signaling pathway to inhibit cholangiocyte differentiation (red T).