Table 1. U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved immunotherapies for advanced urothelial carcinoma.
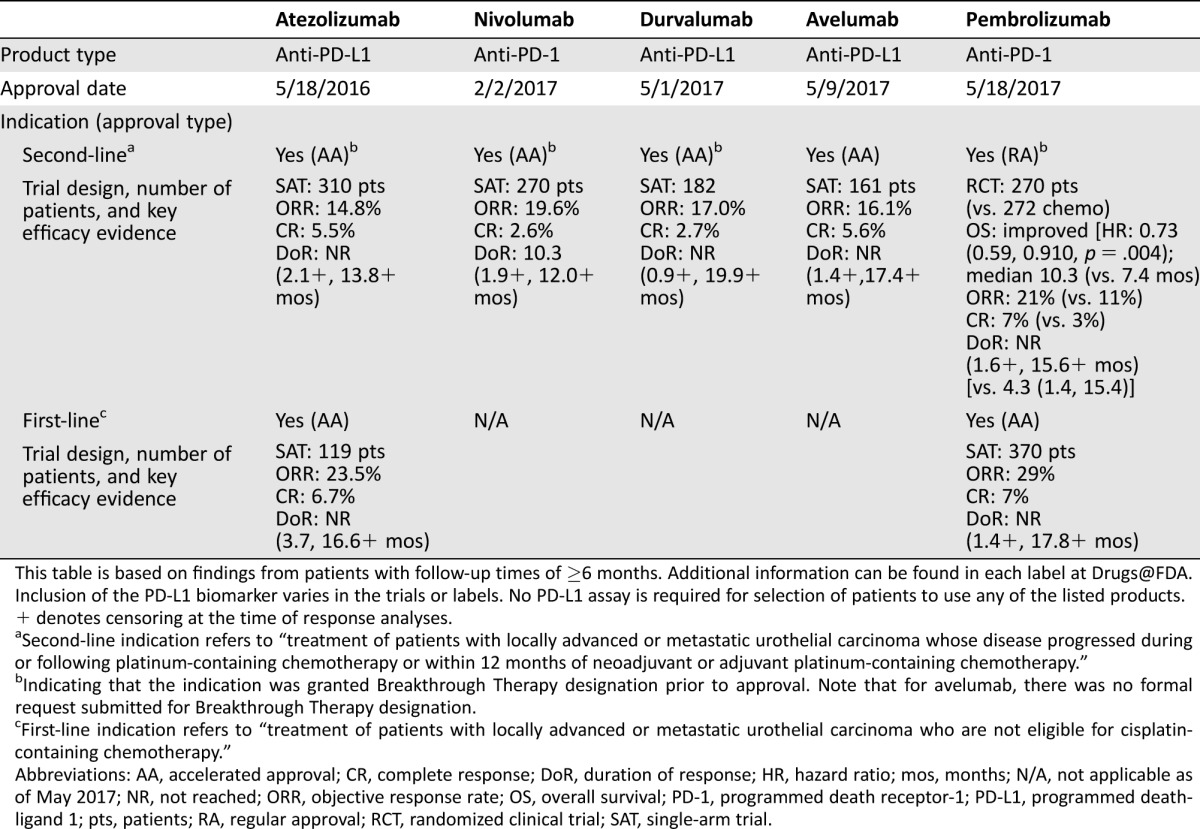
This table is based on findings from patients with follow‐up times of ≥6 months. Additional information can be found in each label at Drugs@FDA. Inclusion of the PD‐L1 biomarker varies in the trials or labels. No PD‐L1 assay is required for selection of patients to use any of the listed products.
+ denotes censoring at the time of response analyses.
Second‐line indication refers to “treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma whose disease progressed during or following platinum‐containing chemotherapy or within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant platinum‐containing chemotherapy.”
Indicating that the indication was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation prior to approval. Note that for avelumab, there was no formal request submitted for Breakthrough Therapy designation.
First‐line indication refers to “treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who are not eligible for cisplatin‐containing chemotherapy.”
Abbreviations: AA, accelerated approval; CR, complete response; DoR, duration of response; HR, hazard ratio; mos, months; N/A, not applicable as of May 2017; NR, not reached; ORR, objective response rate; OS, overall survival; PD‐1, programmed death receptor‐1; PD‐L1, programmed death‐ligand 1; pts, patients; RA, regular approval; RCT, randomized clinical trial; SAT, single‐arm trial.
