Fig. 6.
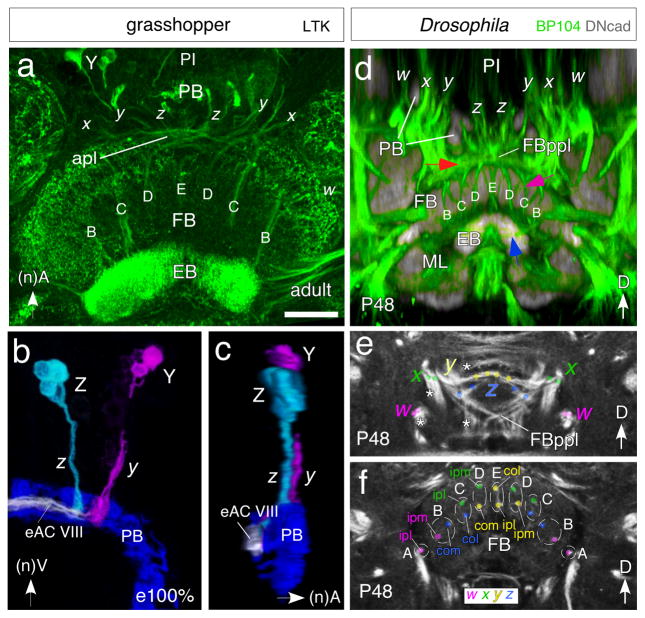
Equivalent organization of tract-based columns in the FB of the grasshopper (a–c) and Drosophila (d–f). a. Confocal image of the central brain region of the adult grasshopper following locustatachykinin (LTK) immunolabeling reveals bilaterally symmetrical tract-specific columns (B, C, D, E) of the FB. Columns comprise axons from cell clusters in the PI projecting via the w, x, y, z system of tracts (x, y, z are visible here) through the PB into the anterior plexus (apl) from which they decussate to the EB. Neuraxes apply to grasshopper panels. b. 3D reconstruction from confocal optical slices following LTK immunolabeling at 100% of embryogenesis shows axons from a small cluster of LTK-positive cells at the equiavelnt location within each Z and Y lineage projecting through the PB and into fascicle eAC VIII of the commisural system. Axons project contralaterally across the midline where they will decussate to form tract-based columns (not shown). False colors have been applied, white indicates superposition of projections. Preparation is viewed from posterior. c. Same preparation as in b but rotated by 90° to reveal the position of fascicle eAC VIII with respect to the PB and z, y tracts. Axons are concurrent (white) in eAC VIII which is the first commissure posterior to the PB. d. Confocal image following double-immunolabeling (BP104, green; DNcad, grey) at the P48 stage of Drosophila reveals axons from lineages in the PI region projecting via the PB into the posterior plexus of the fan-shaped body (FBppl, red arrow) from which they decussate to form the tract-specific columnar system (B, C, D, E, purple arrow) of the FB. These axons then project further (blue arrow) to the EB. Body axes apply to Drosophila panels. Note the conserved projection pattern with that in the grasshopper (c.f. panel a). e, f. Confocal images following BP104 immunolabeling at the P48 stage of Drosophila reveals axon pathways in the central brain originating from w (magenta), x (green), y (yellow) and z (blue) lineages and that contribute to the columnar architecture of the FB. Both panels show frontal sections: (e) corresponds to a posterior level, illustrating the posterior plexus of the fan-shaped body (FBppl); (f) is more anterior at the level of the fan-shaped body (FB). White asterisks in (e) indicate tracts from the w, x, y, z lineages which do not project to the central complex. Colored dots in (e) and (f) demarcate the two bundles contributed by each of the four lineages to the central complex. Bundles of ipsilateral w (magenta) and x (green) and contralateral y (yellow) and z (blue) lineages approach each other as a result of decussation and form pairs corresponding to the A, B, C, D, E columns of the FB. Axon tracing (color coded) reveals that columns A–E comprise combinations of axons from ispsilateral lateral (ipl)-, ipsilateral medial (ipm)-, contralateral medial (com)- or contralateral lateral (col)- w, x, y or z lineages. Scale bar in a represents 80μm in a, 35μm in b, c, 25μm in d–f