Figure 2.
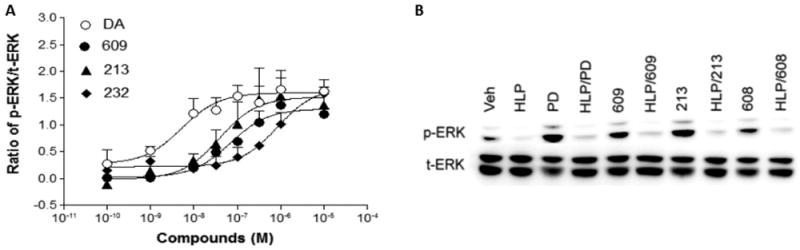
Dose-dependent response of dopamine (DA), SK609, or its analogues and antagonizing effect of antagonist on agonist-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. (A) Dose–response curves of ERK1/2 phosphorylation induced by DA, SK609, SK213, and SK232 at CHO-D3R. CHO-D3R cells were pretreated with vehicle, indicated concentrations of DA, SK609, SK213, or SK232 for 5 min, washed once with PBS buffer, and lysed for Western blots. Signals were quantified by densitometry and normalized to total ERK (t-ERK1/2) and the data is presented as ratio of p-ERK/t-ERK minus vehicle control. The graphs represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (B) Haloperidol (HLP) (1 μM) blocked the activation of ERK1/2 induced by PD128907, SK609, and SK608 at CHO-D3R. This image represents one of three independent Western blot experiments of ERK1/2 phosphorylation (p-ERK1/2) induced by 1 μM of PD128907 (PD), SK609, or its analogues in the presence or absence of 1 μM haloperidol for 5 min, which showed consistent results.
