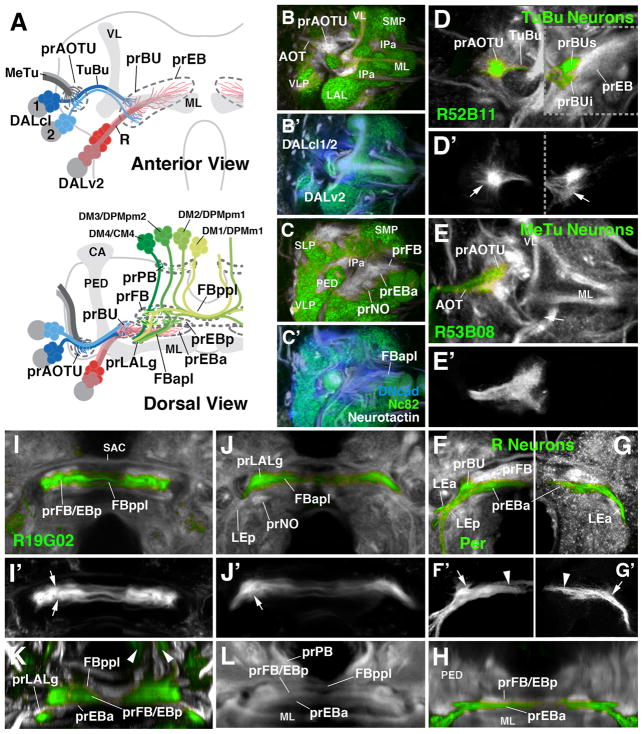
Figure 2.
Larval primordia of the central complex and anterior visual pathway. (A) Schematic view of larval brain hemisphere (top: anterior view, dorsal up; bottom: dorsal view, posterior up). Secondary lineages contributing to the primordia of anterior visual pathway and central complex are rendered in different colors; mushroom body (gray) is shown as reference. (B, B′, C, C′) Z-projections of frontal confocal sections of late larval brain hemisphere labeled with anti-Bruchpilot (Nc82; green), anti-DN-cadherin (DNcad; white in B, C; blue in B′, C′) and anti-Neurotactin (BP106; white in B′, C′). Note domains which are negative for Nc82, indicating absence of synapses; these domains are positive for DNcad and BP106, showing presence of (undifferentiated) secondary fibers and filopodia which make up primordia of adult-specific compartments. Labeled are primordia of anterior optic tubercle (prAOTU), anterior ellipsoid body (prEBa), bulb (prBU), fan-shaped body (prFB), noduli (prNO. (D–K): Z-projections of confocal sections of late larval brain hemispheres in which individual cell classes forming part of anterior visual pathway and central complex are labeled by specific Gal4 drivers (green). In (D–L), DNcad antibody labels neuropil (white); (D′–G′) show only GFP expression. (D–G′) and (I, J) show frontal sections, (H) and (K, L) are digitally tilted dorsal views. (D, D′) Tuberculo-bulbar (TuBu) neurons of DALcl1/2 lineages, labeled by R52B11-Gal4. Shown to the left of hatched line is a more anterior plane, containing tufts of proximal filopodia (marked by arrow in D′) that constitute the primordium of the anterior optic tubercle. To the right of the hatched line is a slightly more posterior plane, featuring endings and distal filopodia of TuBu neurons, which form the primordia of the superior and inferior bulb (prBUs, prBUi), respectively. (E, E′) Axonal endings of medullo-tubercular (MeTu) neurons in the primordium of the anterior optic tubercle, labeled by R53B08-Gal4. (F–H) Ring (R) neurons of DALv2 lineage, labeled by Period (Per)-Gal4 (F, F′, H) or as MARCM clone (G, G′). DALv2 neurons form a straight, medially-directed bundle, the anterior lateral ellipsoid body tract (LEa), which extends posterior to the medial lobe of mushroom body (ML in panel A) to end close to the midline. Filopodial tufts of these axons form the primordia of the anterior ellipsoid body (prEBa; arrowheads in F′, G′) and, further laterally, the bulb (prBU; arrows in F′, G′). (I–L) Subset of columnar neurons of the central complex, labeled by R19G02-Gal4. These neurons form part of four type II lineages, DM1/DPMm1, DM2/DPMpm1, DM3/DPMpm2, DM4/CM4, as shown in panel (A). Axons project forward and proximal filopodia form the primordium of the protocerebral bridge (arrowheads in K; prPB in A). Axons then branch and turn medially, forming the posterior plexus of the fan-shaped body (FBppl in A, I, K). Filopodial tufts branch in the primordium of the fan-shaped body (A, I, K) and the posterior ellipsoid body (prFB/EBp in I, K). Axons continue forward, branching towards medially and laterally, forming the anterior plexus of the fan-shaped body (FBapl; A, J). Distal tips of this projection defines the primordium of the gall of the LAL (prLALg; A, J, K). For other abbreviations, see List of Abbreviations. Bar: 25μm