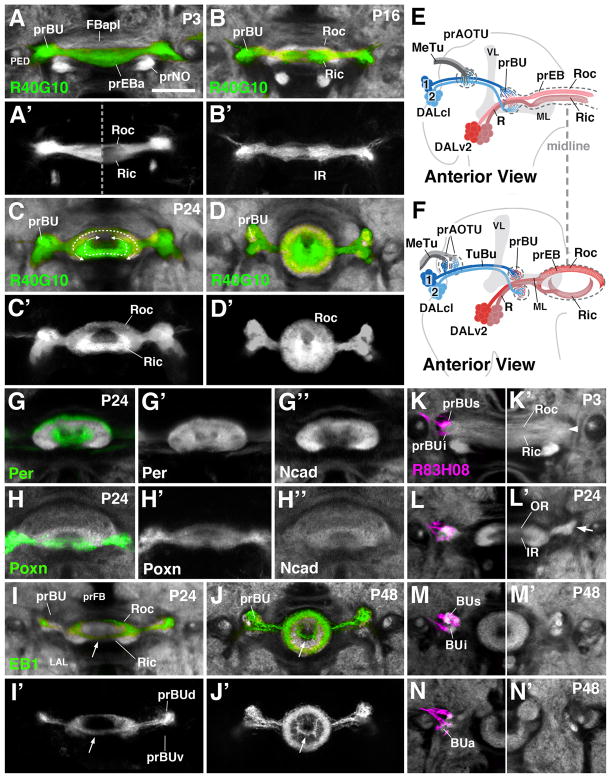
Figure 3.
Morphogenesis of the ellipsoid body and bulb. (A–D′) and (G–N′) Z-projections of frontal confocal sections of pupal brain hemispheres at different stages, indicated in upper left corner of panels (P3 3hrs after puparium formation (APF); P16 16hrs APF; P24 24hrs APF; P48 48hrs APF). In panels (A–D) and (G–N), specific neuron populations are labeled by Gal4-drivers indicated at lower left corner of panels; antibody against DN-cadherin marks neuropil (white). (A–D′) R40G10-Gal4 labels preferentially inner ring (Ric) neurons throughout development. (E, F) Schematic anterior view of pupal brain hemisphere at 6hrs (E) and 24hrs (F) after puparium formation (APF). Secondary lineages contributing to the primordia of the anterior visual pathway are rendered in different colors; mushroom body (gray) is shown as reference. (G–H″) Per-Gal4 and Poxn-Gal4 are expressed in all R-neurons, but allow one to distinguish the inner from outer ring during early pupal stages. (I–J′) EB1-Gal labels R2 class of outer ring neurons. (K–N): R83H08-Gal4 (magenta) is expressed in tuberculo-bulbar neurons and labels the developing bulb primordium (prBUs, prBUi, prBUa) of left brain hemisphere. Panels (K′–N′) show opposite hemisphere, labeled only with anti-DN-cadherin (white). For other abbreviations, see List of Abbreviations. Bar: 25μm