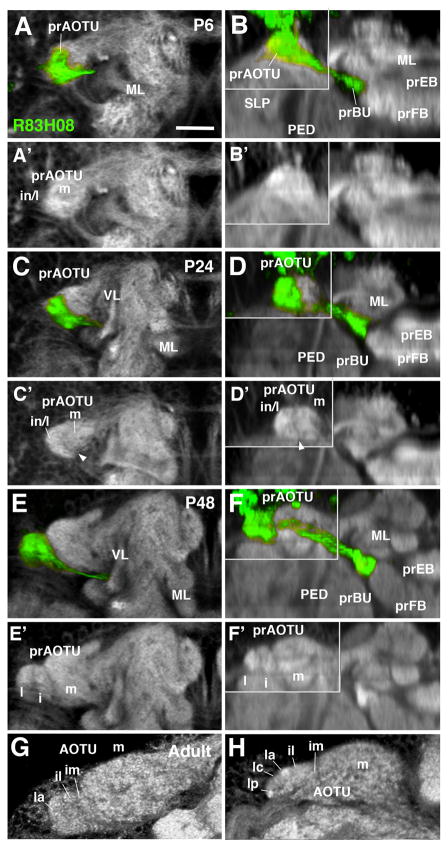
Figure 4.
Morphogenesis of the anterior optic tubercle. Panels show Z-projections of frontal confocal sections (left column; A, C, E, G) and corresponding, digitally-tilted horizontal sections (right column; B, D, F, H) of brain hemisphere at different stages of development, from 6hrs APF (P6) to Adult (stages indicated in upper right corner of panels). In panels of right column, the area in upper left boxed by gray line represents a dorsal level, including the prAOTU; remainder of the panels show horizontal sections at a more ventral level, including the prBU. Proximal arborizations of TuBu neurons, labeled by R83H08-Gal4 (green), mark the developing primordium of the anterior optic tubercle (prAOTU); distal arborizations outline the primordium of the bulb (prBU). Neuropil is labeled by anti-DN-cadherin (white). In early pupa (P6; A–B′) the prAOTU forms an undifferentiated, ovoid, DN-cadherin-rich domain at the anterior-lateral surface of the superior lateral protocerebrum (SLP). GFP-positive fibers of TuBu neurons are largely restricted to the lateral half of the prAOTU (A), which will give rise to the intermediate and lateral subdomains of this compartment (in/l in A′). The medial part of the prAOTU (m in A′) does not receive GFP-positive fibers. At P24 (C–D′), a sharp boundary separates the medial from the intermediate/lateral subdomain (arrowhead in C′, D′). At P48 (E–F′), the GFP-positive domain has differentiated into a lateral (l) and intermediate (i) subdomain. During late pupal development, these become further subdivided into smaller subdomains, including the intermediate medial (im), intermediate lateral (il), lateral anterior (la), lateral central (lc), and lateral posterior (lp; G, H). For other abbreviations: see List of Abbreviations. Bar: 25μm.