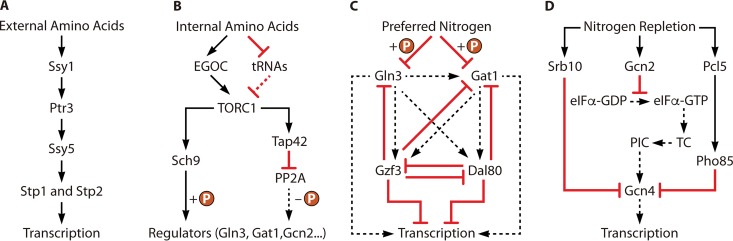
FIG 7.
Outline of pathways involved in nitrogen regulation in S. cerevisiae. (A) Pathway of the SPS sensor system mediated by sensing of external amino acids. Ssy1 is activated by external amino acids. The signal is transduced by Ptr3 and activates Ssy5. The activated Ssy5 is responsible for activating two transcriptional factors, Stp1 and Stp2. Finally, Stp1 and Stp2 activate the transcription of relevant genes. (B) Pathway of TOR pathway mediated by sensing of internal amino acids. The accumulation of internal amino acids promotes the establishment of the EGOC and decreases the internal abundance of tRNAs. As a result, TORC1 is activated by the EGOC and derepressed by the reduction of internal tRNAs. Next, the downstream effectors Sch9 and Tap42 are activation by activated TORC1. Finally, the phosphorylation of regulators, such as Gln3, Gat1, and Gcn2, is induced by Sch9. In addition, activated Tap42 promotes its interaction with PP2A, which represses the PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of regulators. (C) Transcriptional regulatory pathway mediated by NCR. The major activators of NCR, Gln3 and Gat1, are phosphorylated in the presence of preferred nitrogen sources. As a result, the transcriptional activation mediated by these two activators is repressed. (D) Regulation of the GAAC pathway responds to nitrogen sources. Gcn2 is activated under nitrogen repletion conditions, which then represses the transformation of eIF2α from a GDP- to a GTP-bound status. The reduction of eIF2α-GTP decreases the TC, which then inhibits the formation of the PIC. As a result, the translation of GCN4 mRNA is repressed, leading to a decreased intracellular concentration of Gcn4. On the other hand, nitrogen repletion conditions also induce the degradation of the Gcn4 through activation of Srb10. In addition, nitrogen repletion also induces the activation of Pcl5, which then activates Pho85 and finally induces the degradation of Gcn4. The decrease of Gcn4 finally represses the transcriptional activation of relevant genes dependent on Gcn4.