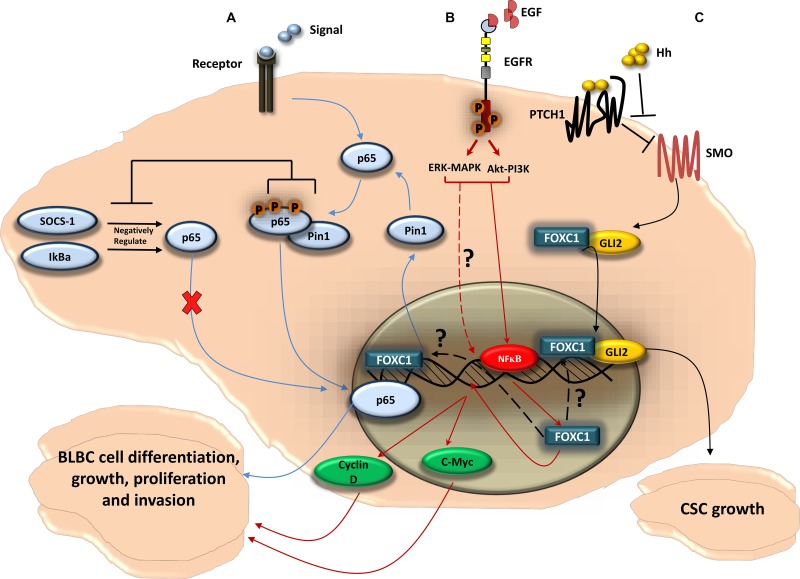
Figure 3. FOXC1-signaling pathways in BLBC.
(A) FOXC1 regulates the function of the NF-κB pathway in BLBC cell; NF-κB pathway can be activated as a cellular response to stimuli. Once activated, the NF-κB subunit p65 get phosphorylated and translocated to the nucleus where it binds to DNA. The p65 activity is negatively regulated by the ubiquitin ligase cytokine signal inhibitor SOCS-1 [133] that sends p65 to the proteasome for degradation, and by IκBα that plays a role in the steady-state cytoplasmic localization of p65 dimers, thus preventing p65 nuclear localization and DNA binding [134]. The NF-κB pathway activity has been linked to tumorigenesis. In BLBC cell, FOXC1 regulates the expression of Pin1, a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, that regulates the activity of p65 [133] and has been linked to tumor development [135]. Pin1 physically binds to p65 in the cytoplasm. This physical binding thus blocks p65 association with SOCS-1 and IκBα, as a result inhibits the p65 degradation. This then leads to p65 phosphorylation and p65 translocation to the nucleus. p65 binds to DNA and activates genes that enhances BLBC cell growth and proliferation. (B) EGFR, via MAPK-ERK and PI3K-Akt pathways, upregulates FOXC1 in BLBC; upon activation of EGFR by the ligand EGF, two of the classical pathways Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) and Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K) can be activated. The PI3K and MAPK pathways thus upregulate FOXC1 protein and mRNA expression through the ERK and Akt proteins. It has been shown that Akt and ERK phosphorylate and activate NF-κB that leads to its translocation to the nucleus [130]. NF-κB then would bind to FOXC1 promoter region and increases FOXC1 transcription activity. FOXC1 then would enhance the expression of the transcription factor c-Myc and Cyclin D, in which both play a key role in BLBC cell growth, proliferation, and invasion. (C) FOXC1 activates Smoothened-independent Hedgehog Signaling; the ligand Hh binds to the receptor Patched 1 (PTCH1) which allow SMO to activate the transcription factor Glioma-Associated Oncogene Family Zinc Finger 2 (GLI2). FOXC1 can activate GLI2 independently from SMO, where the FOXC1 N-terminal domain (aa 1-68) binds directly to a certain internal region of GLI2 (aa 898-1168), increasing GLI2-DNA transcription activity. FOXC1 activation of the non-canonical Hh signaling can result in cancer stem cell growth and expansion, consequently produces the BLBC stem-like phenotype.