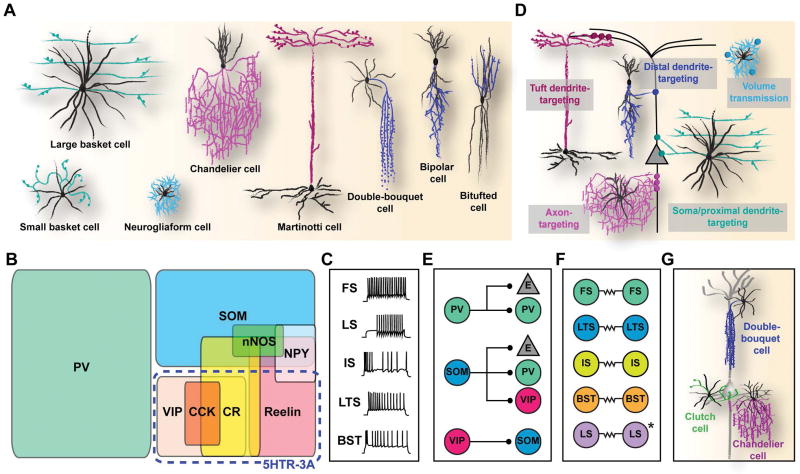
Figure 1. Multiple dimensions of cortical interneuron diversity.
(A) Morphologically defined subtypes of interneurons. Black and colored lines represent dendritic and axonal processes, respectively. Inspired from Schmolesky, M. 1995.149 (B) Classification of subtypes based on molecular marker expression. PV, parvalbumin; SOM, somatostatin; VIP, vasointestinal peptide; CR, calretinin; CCK, cholecystokinin; NPY, neuropeptide Y; 5HTR-3A, serotonin receptor 3A. (C) Electrophysiological classification of interneurons based on the action potential response pattern upon electrical stimulation. Adapted from Markram, H. et al., 2004.2 FS, fast spiking; LS, late spiking; IS, irregular spiking; LTS, low-threshold spiking; BST, bursting. (D) Diversity in subcellular targeting. (E) Diversity in cellular targeting. E, excitatory neuron. (F) Patterns of electrical synapse formation in different interneuron subtypes. (G) Morphologically-defined subtypes that are particularly numerous and refined in primates.