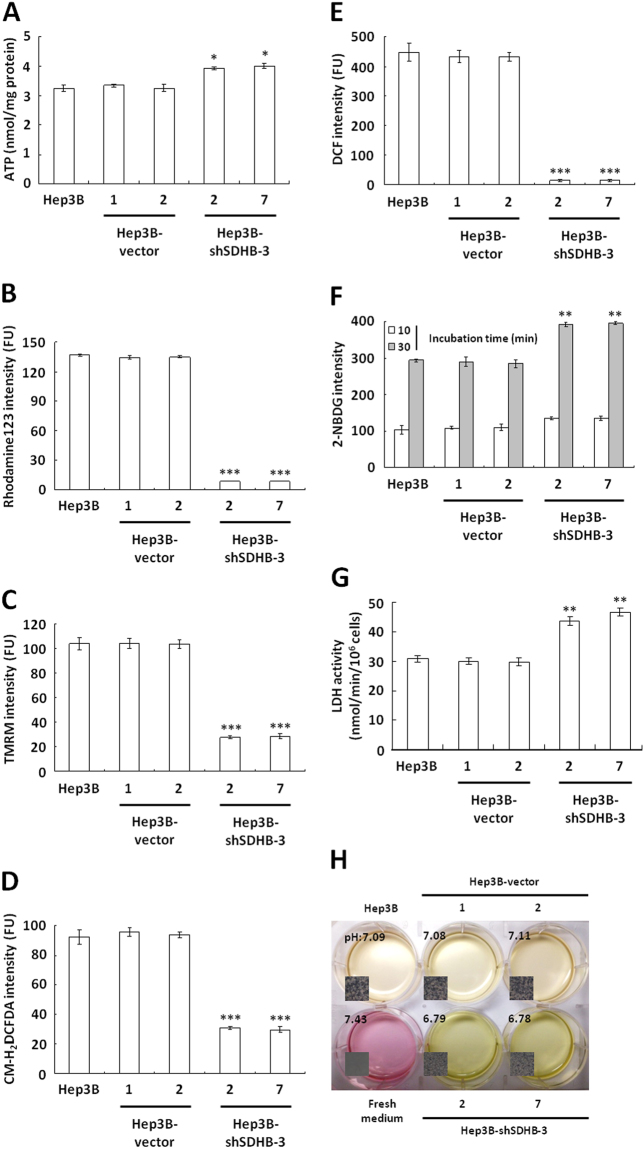
Figure 3.
SDHB knockdown causes severe defects in mitochondrial respiration but increases glucose uptake and glycolytic metabolism. (A) ATP assay in SDHB-knockdown cells. Total extracts prepared from cells as indicated were subjected to an ATP assay using the ATP Bioluminescence Assay Kit CLSII. (B,C) Δψm assay of SDHB-knockdown cells. Cells as indicated were stained with Rhodamine123 and TMRM and then analyzed using a flow cytometer. (D,E) ROS assay of SDHB-knockdown cells. Cells were treated with CM-H2DCFDA and DCF as indicated and subsequently analyzed using a flow cytometer. (F) Glucose uptake assay of SDHB-knockdown cells. Cells as indicated were loaded with 2-NBDG and then analyzed using a flow cytometer. (G) LDH activity assay of SDHB-knockdown cells. Total extracts prepared from cells were subjected to a LDH activity assay using the CytoTox 96® Non-Radioactive Cytotoxicity Assay. (H) Color change and pH measurements of the conditioned media cultured with SDHB-knockdown cells. Cells as indicated were cultured until confluent and then incubated in fresh media for 12 h. The color and pH of the conditioned media were imaged and measured. The *, ** and *** represented P-value < 0.05, <0.01 and <0.005, respectively.