Fig. 2.
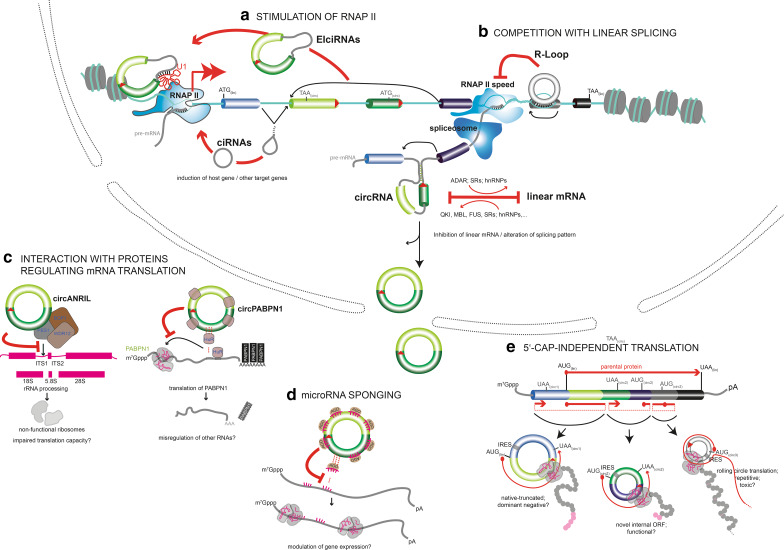
Cellular functions of circRNAs in eukaryotes. a, b Nuclear functions of circRNAs. a EIciRNAs and ciRNAs stimulate RNAP II-dependent transcriptional initiation at the transcriptional start site of a protein-coding gene in the nucleus. Potential roles in elongation are not depicted. b Top: stimulation of parental exon-skipping by DNA-binding circRNAs that form a DNA:RNA hybrid (R-loop) that can impair RNAP II. Bottom: backsplicing in the pre-mRNA antagonizes the production (and/or stability) of the colinearly spliced linear host mRNA. c–e Cytoplasmic functions of circRNAs. c Interaction of circRNAs with proteins and inhibition of their normal functions. Two unrelated cases are shown, binding of circANRIL to PES1 for inhibiting the PeBoW complex during rRNA processing (left) and the sponging of the HuR protein by circPABPN1 (right). d circRNAs can also sponge microRNAs and thereby inhibit the translational blockage in mRNAs targeted by these microRNAs (whether binding is occuring only in the cytoplasm is not known). e Translation of ORFs encoded on circRNAs by 5′Cap-independent initiation using either IRES or, hypothetically, m6A methylation (not shown). See text for details