Fig. 5.
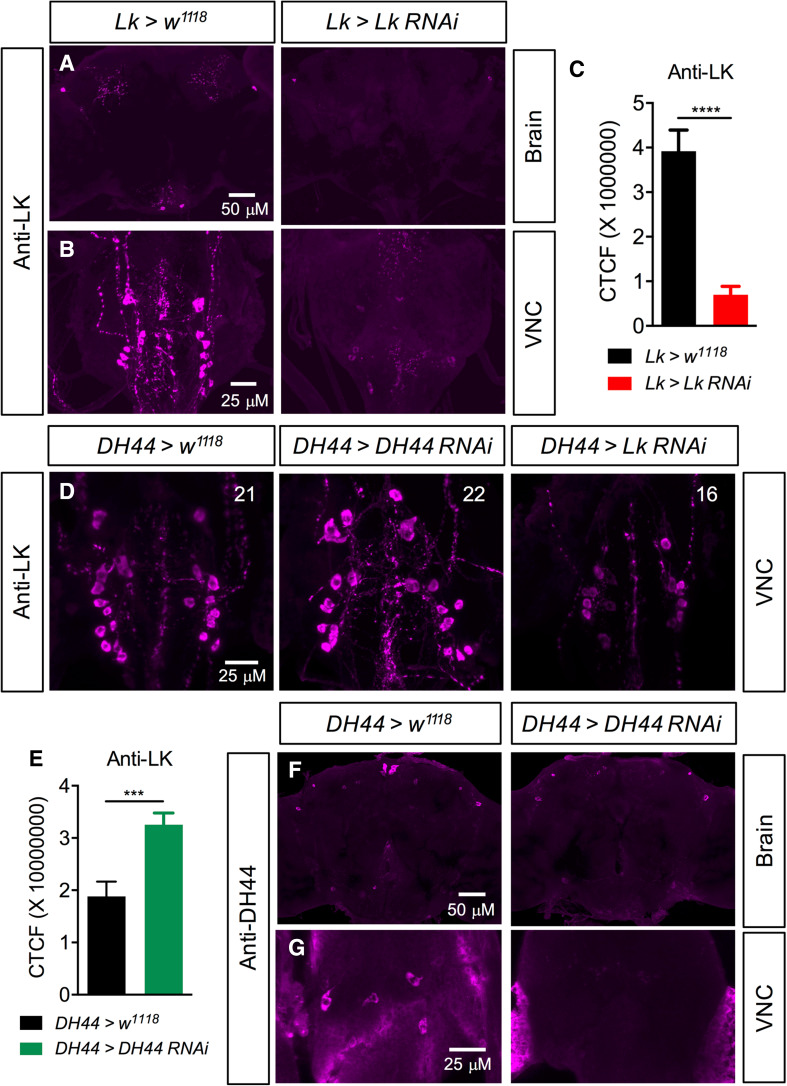
Lk- and DH44-RNAi knockdown efficiency was tested using immunolabelling. a, b Knockdown of Lk with Lk-GAL4driven Lk-RNAi causes a significant decrease in LK-immunoreactivity in the adult brain and ventral nerve cord (VNC). ****p < 0.0001, as assessed by unpaired t test. c Fluorescence intensity measurement of lateral horn LK neurons shows a significant decrease in LK-immunoreactivity in Lk knockdown flies compared to control flies. CTCF corrected total cell fluorescence. d DH44-GAL4-driven Lk-RNAi causes a significant decrease in LK-immunoreactivity in the adult VNC as determined by the number of immunoreactive neurons (the average number of neurons is indicated in each panel; see Figure S6) that could be detected. However, DH44-GAL4-driven DH44-RNAi causes a significant increase in LK-immunoreactivity in adult ABLKs (***p < 0.001, as assessed by unpaired t test). (e) and a complete abolishment of DH44-immunoreactivity in the adult brain (f) and VNC (g)