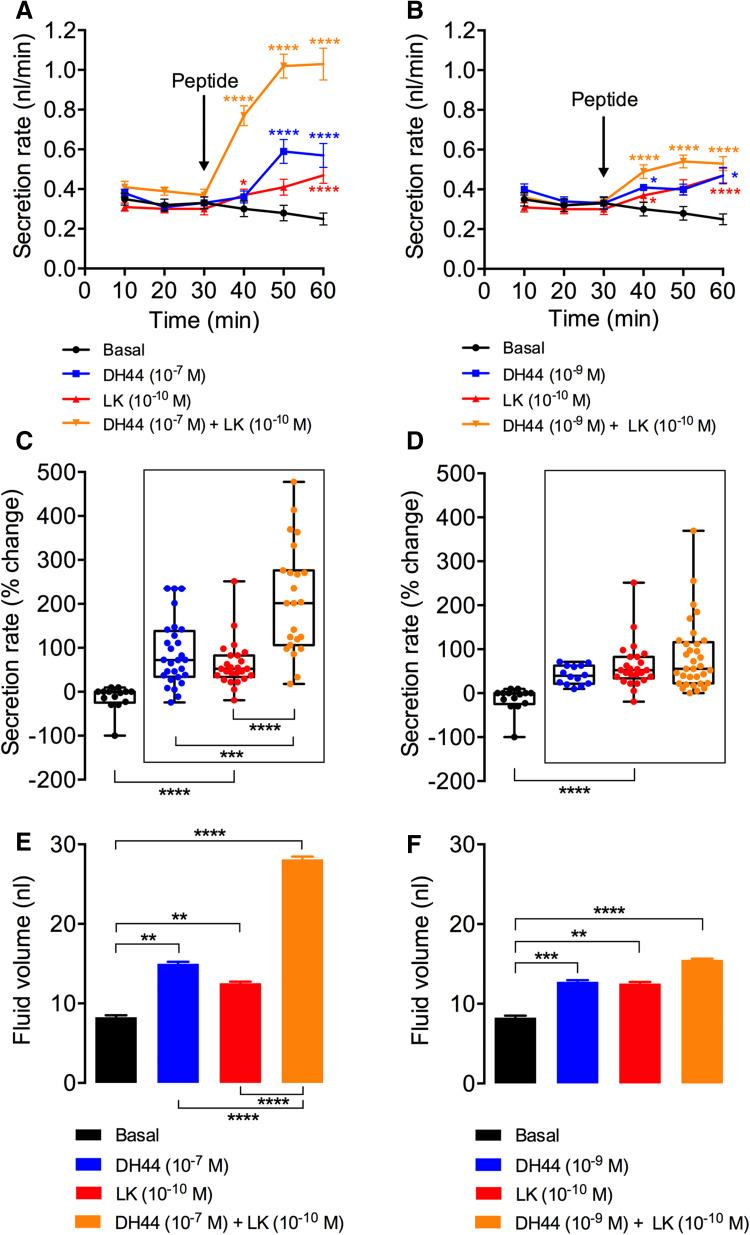
Fig. 9.
LK and DH44 peptide application results in an additive response on fluid secretion by Malpighian tubules (MTs) ex vivo. a Secretion rates of MTs incubated with 10−7 M DH44 (n = 28), 10−10 M LK (n = 25), a combination of both 10−7 M DH44 and 10−10 M LK (n = 23), or no treatment/basal (n = 14). b Secretion rates of MTs incubated with 10−9 M DH44 (n = 14), 10−10 M LK (n = 25), a combination of both 10−9 M DH44 and 10−10 M LK (n = 31), or no treatment/basal (n = 13). For both a and b, secretion rates were measured at 10 min intervals for 30 min before and after the addition of peptide (indicated with an arrow). Asterisk indicates significantly different secretion rate compared to basal secretion rate (secretion rate prior to the addition of peptide. For further statistics, see Table 4. c, d Change (%) in secretion determined by comparing the secretion rate over the first 30 min to the maximum secretion rate following peptide application. The legend and sample size for c and d are the same as the one in a and b, respectively. e, f Total fluid secreted for 30 min following peptide application or no treatment (basal). Note that the amount of total fluid secreted following the addition of both LK (10−10 M) and DH44 (10−7 M) is a sum of the total fluid secreted following the addition of each of those peptides separately. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; Mann–Whitney U test)