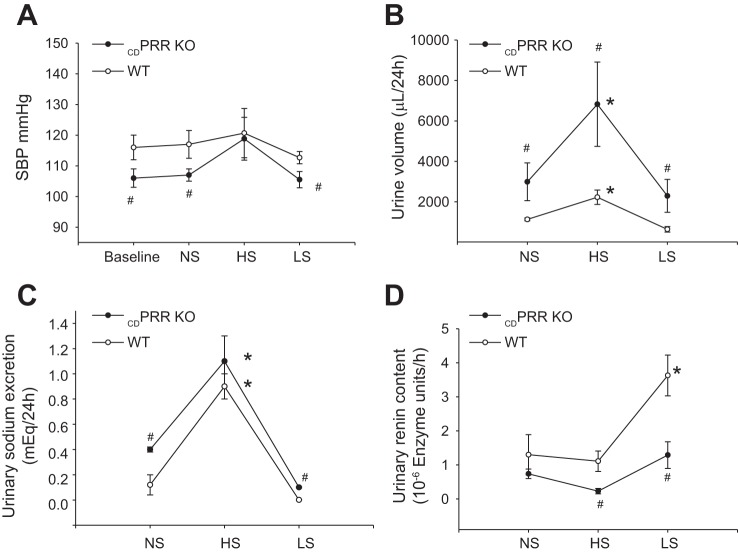
Fig. 2.
Physiological responses to changes in dietary salt in wild-type (WT, n = 8) and CDPRR-KO mice (n = 6). A: systolic blood pressure (SBP) measured by tail-cuff method at baseline during three consecutive days on normal-salt (NS), high-salt (HS), and low-salt (LS) diets. B: urine volume was higher in KO mice than WT during NS, HS, and LS diets. C: urine sodium excretion was higher in CDPRR-KO mice than WT at baseline and LS conditions. D: importantly, during LS diet, the content of active renin in the urine was augmented in WT mice but not in CDPRR-KO mice. Measurements were done by day 3 on each diet. Interactions among genotypes are reported according to the two-way ANOVA (#P < 0.05 vs. WT mice), and differences between treatments are reported (*P < 0.05 vs. baseline).